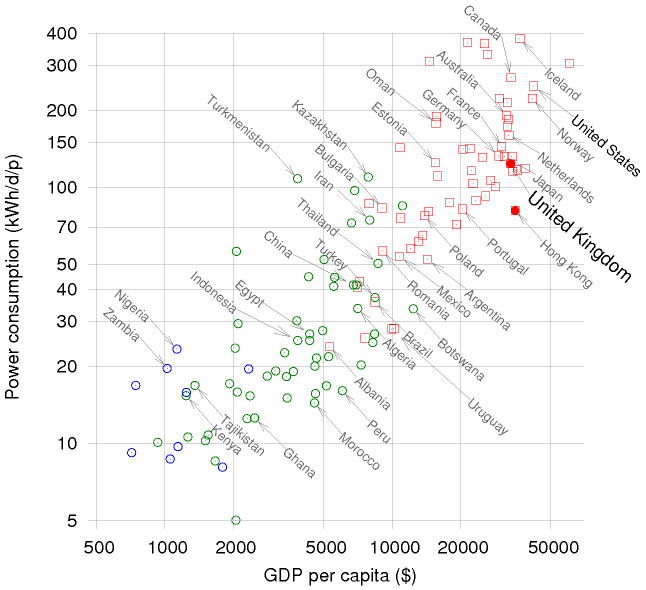
Energy and GDP
There is a correlation between energy use and the gross domestic product in countries.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Monetary value of all goods and services created by an economy.
- Per capita GDP (GDP per person)
- The GDP of an economy divided by the number of persons in that economy.
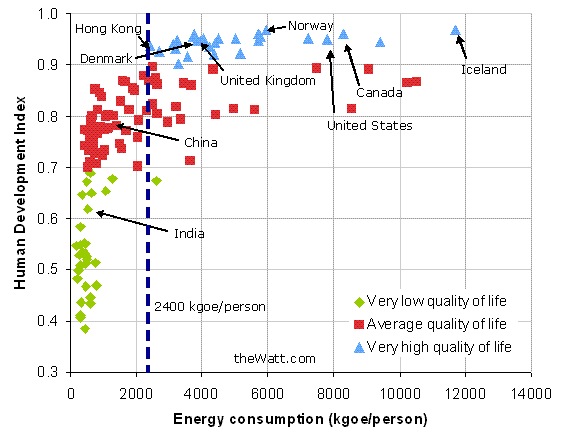
Energy and the Human Development Index
Energy use is correlated with quality of life in many countries. However, improvements in this quality of life (HDI) level off at higher levels of energy consumption.
Market
A system that allows for multiple parties to participate in exchange
We have several energy markets
The free market rests on several assumptions that are not true in practice
For all their power and vitality, markets are only tools. They make a good servant but a bad master and a worse religion. - Amory Lovins, Natural Capitalism
Market Efficiency
Economic theory holds that properly functioning markets deliver the optimal amount of goods at the optimal price to maximize overall benefit.
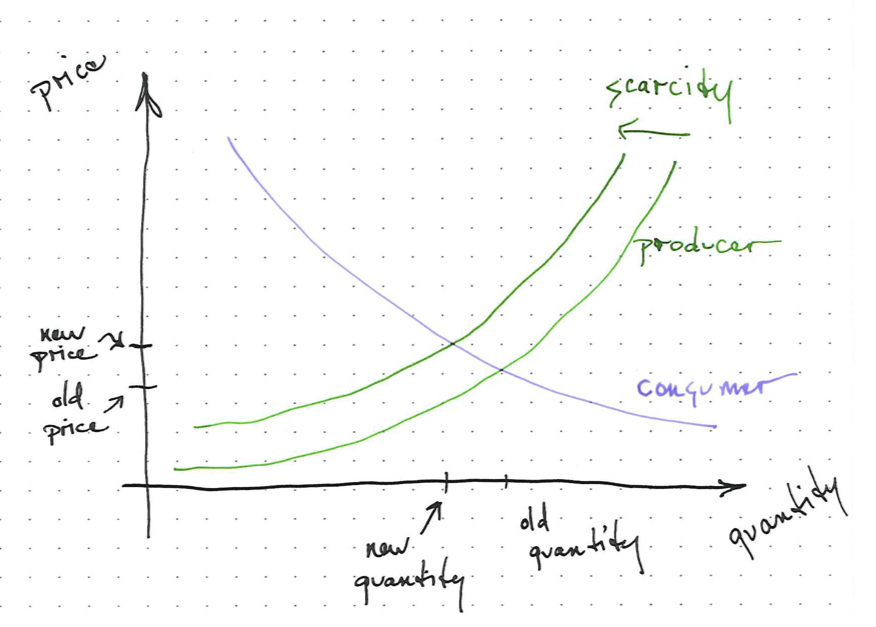
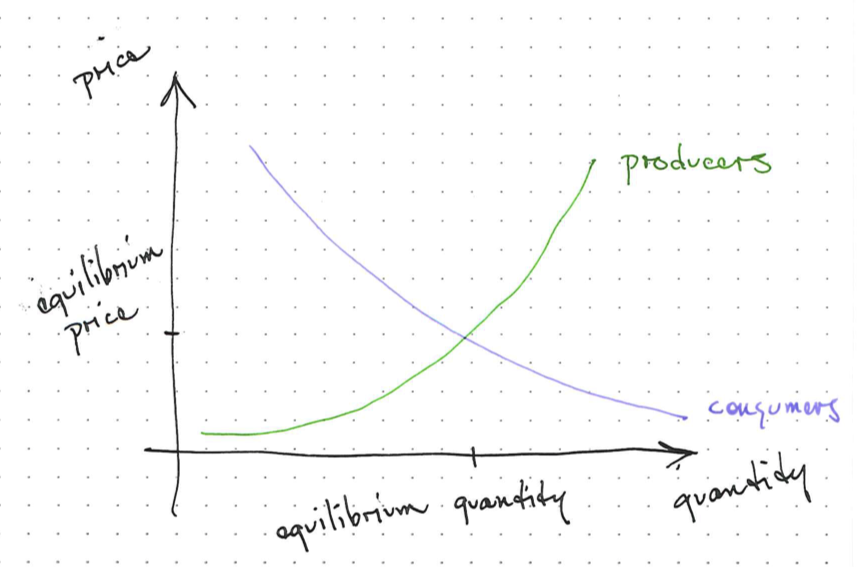
Supply and Demand
The supply and demand model predicts the optimum price and amount at the intersection of supply and demand curves.
Supply Curve
- Marginal Private Cost (MPC)
Demand Curve
- Marginal Private Benefit (MPB)
Externality
A cost or benefit to parties outside of the transaction.
Social Costs and Benefits
- Marginal External Benefit (MEB)
- Marginal Social Benefit (MSB = MPB + MEB)
- Marginal External Cost (MEC)
- Marginal Social Cost (MSC = MPC + MEC)
The optimal price and quantity when we only consider private benefits is different than when we include social benefits.
Social Cost of Carbon
Academics and governments have attempted to compute the social cost or externality associated with a ton of carbon dioxide.
Subsidy and Taxes
If we want to change the amount of a good or service that is provided, we must change the intersection of the supply and the demand curves.
We do this by lowering or raising the price of a good.
For example, if the government creates a carbon tax, the price of gasoline will rise, and there will be less gasoline sold and less carbon emitted.
If instead we want more electric cars, the government can provide a subsidy to electric cars that lowers the price and the market will produce more cars.