Hydropower
Energy Conversion
- Solar radiation evaporates water
- Wind currents from solar air heating move evaporated water to locations where it falls as rain
- Gravity carries water down hill
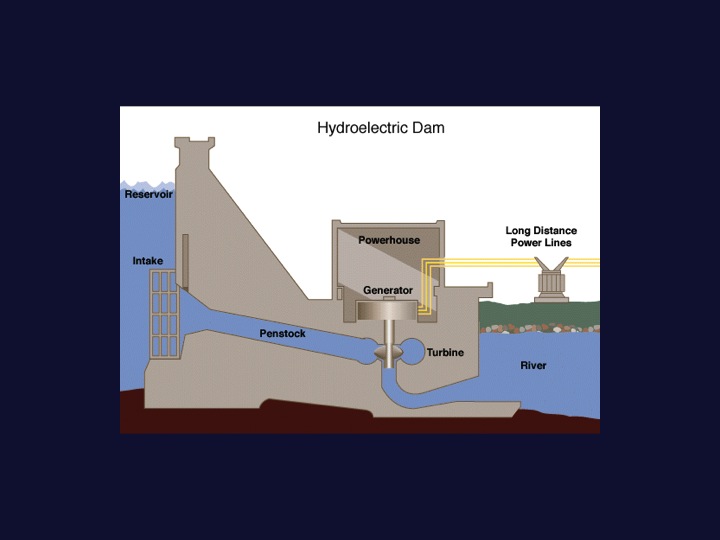
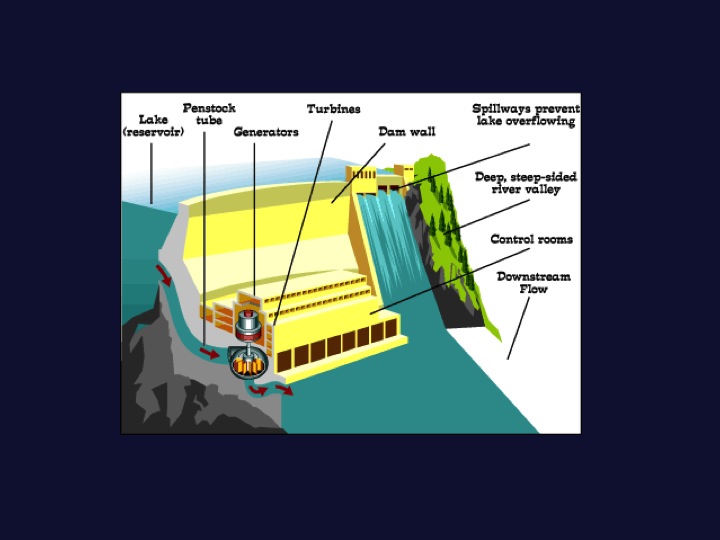
- Hydropower uses this gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy of the water to spin a turbine
- The turbine is connected to a generator, creating electricity
Ancient Power Technology
- Waterwheels have been used for centuries
- Modern hydropower technology has added large scale dams
Energy basics
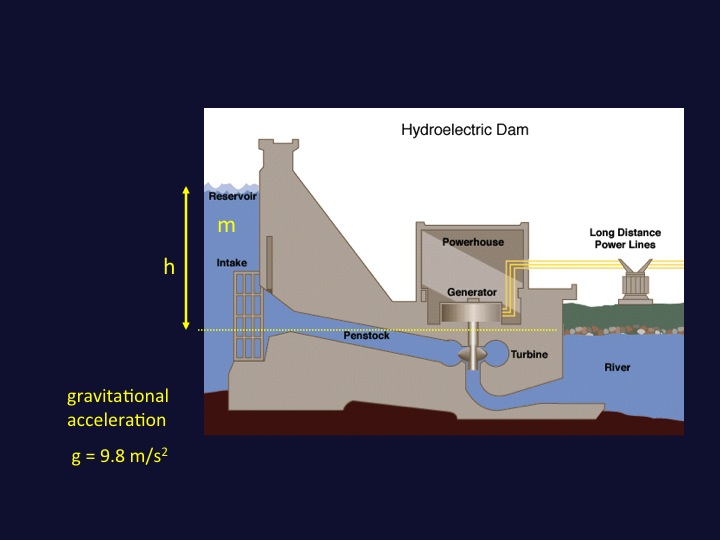
- We use the simplest model for the water as a mass at a height or elevation
- A mass m lifted to a high h has a stored gravitational potential energy of PE = mgh
- PE is in joules if mass is in kilograms, g = 9.8 m/s2 and the height is in meters
Power
- How do we convert this to a power? energy = mgh \frac{energy}{time} = \frac{mgh}{time} power = \frac{m}{time} gh power = flow \cdot gh
- To get flow in mass per time we convert from volume per time
Types
- Run of river
- Dams
Hydropower is significant world wide
- http://wdi.worldbank.org/table/3.7
- 2010 Hydropower 15.9% of world wide electricity
- Coal 40.5%, Nuclear 12.8%
- Largest power station in the world is hydroelectric
Three Gorges
- Largest power plant in the world
- Displaced millions of people
- 22 GW power continuous
- NYC - 10 GW
Three Gorges
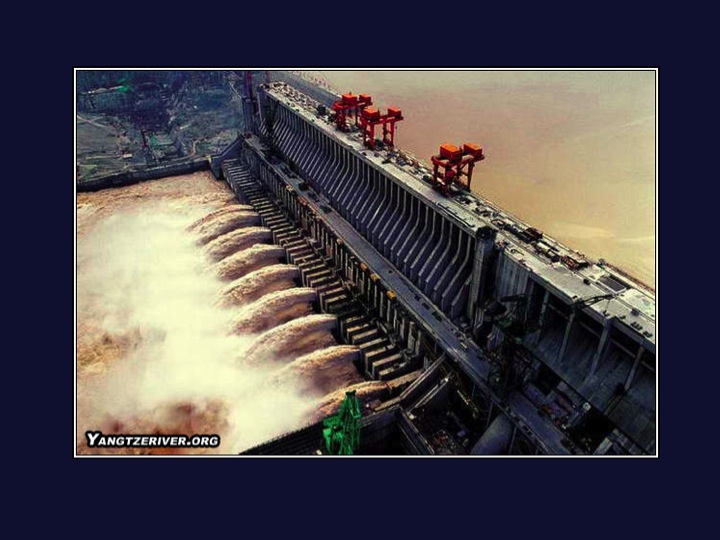

Three Gorges
Grand Coulee
- Largest hydroelectric installation in US
- 6.8 GW capacity
- 21 Billion kWh annual energy delivered
Building a dam
- What is the effect of a dam?
- How does the dam affect the overall flow of water?
Advantages
- Once built, very cheap power
- Reliable technology
- Can be used as storage
Disadvantages
- Fish migration
- Environmental impacts
- Seasonal variation affects electricity supply
- Water flow
- Sedimentation
- Increased seismic activity
- Risk of dam failure
- Methane production from vegetation decomposition
- Methane is a potent GHG
Carbon Intensity of Electricity
Methane generation has a large effect on the greenhouse gas intensity of hydropower electricity.
- Run of river 0.01 – 0.03 lb CO2/kWh
- Dam, Arid region 0.06 lb CO2/kWh
- Dam, Tropical region 0.5 lb CO2/kWh
Source: IPCC 2011 Report, Chapter 5 and 9
Hydropower

Hydropower
Hydropower
Hydropower
Hydropower similarities to fossil generation
- Uses spinning generators just like combustion plant
- Doesn’t use heat, unlike combustion plant
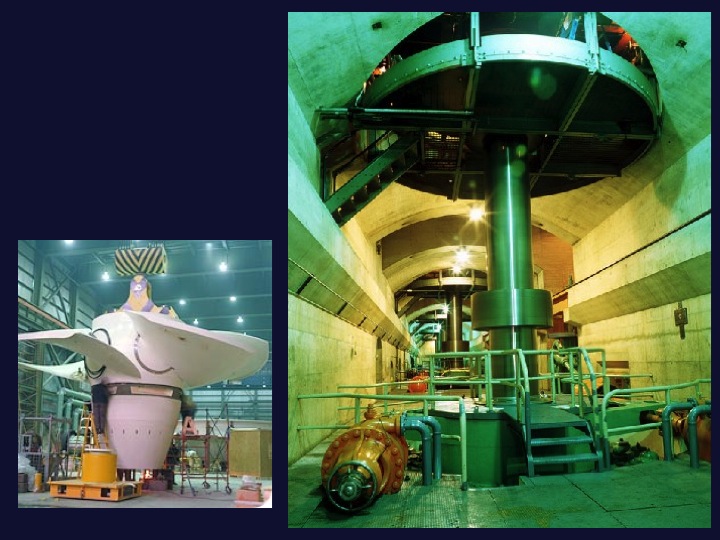
Hydropower turbines

Hoover Dam
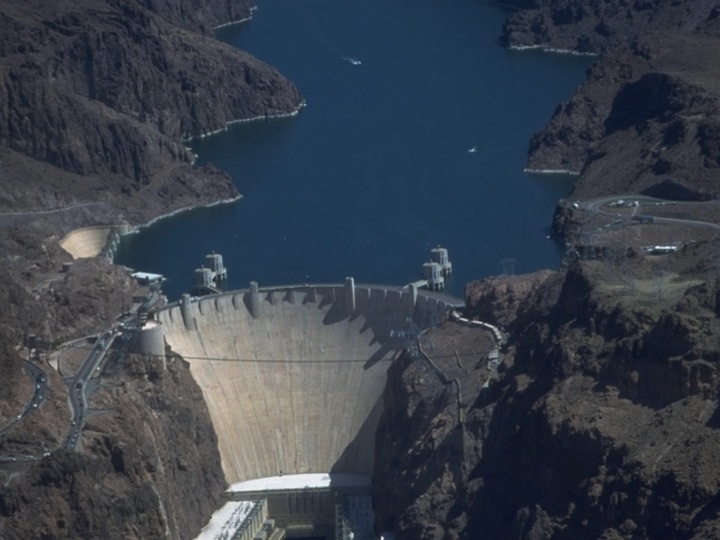

Hoover Dam

Scalability
- Hydropower can be produced at small scale
Hydropower

Hydropower
