Fossil fuels
- Fossil fuels are the product of millions of years of photosynthesis stored and processed under heat and pressure
- Most fuel is found in rocks from about 50-450 million years ago
Review
- Energy basics
- Estimation techniques
- Laws of thermodynamics
- Carbon, photosynthesis, and combustion
Internal Combustion Engines
- Combustion: Gasoline and Oxygen
- Expansion: Combustion gasses expand
- Linear Kinetic Energy: pushes on piston
- Rotational Kinetic Energy: piston pushes on crankshaft
Energy Density
The energy released per mass or volume of fossil fuels is given by the energy density.
Fossil Fuels
- where do we get them
- how do we use them
- why are they useful
- how are they harmful
- fossil fuel etymology latin fodere dig fossilis dug up
Types of Fossil Fuels
- Coal
- Petroleum
- Natural Gas
Impacts of a Global Fossil Fuel Network
- Fossil fuels are being extracted, processed, and used all over the world
- Who bears the burden of the consequences?
- Who benefits from their use?
- Where are these consequences located?
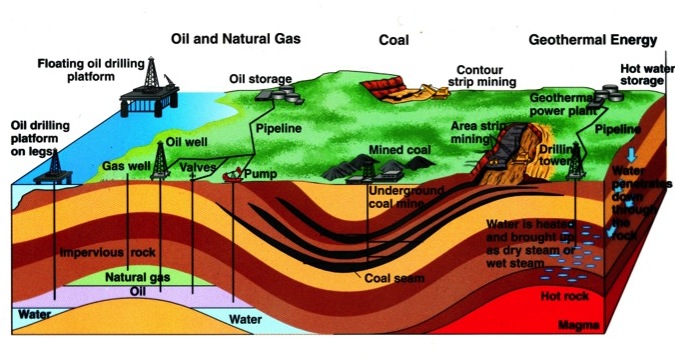
Origin of Fossil Fuels
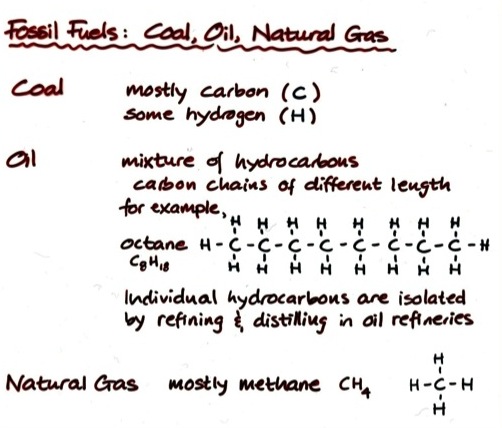
Fossil Fuel Molecules
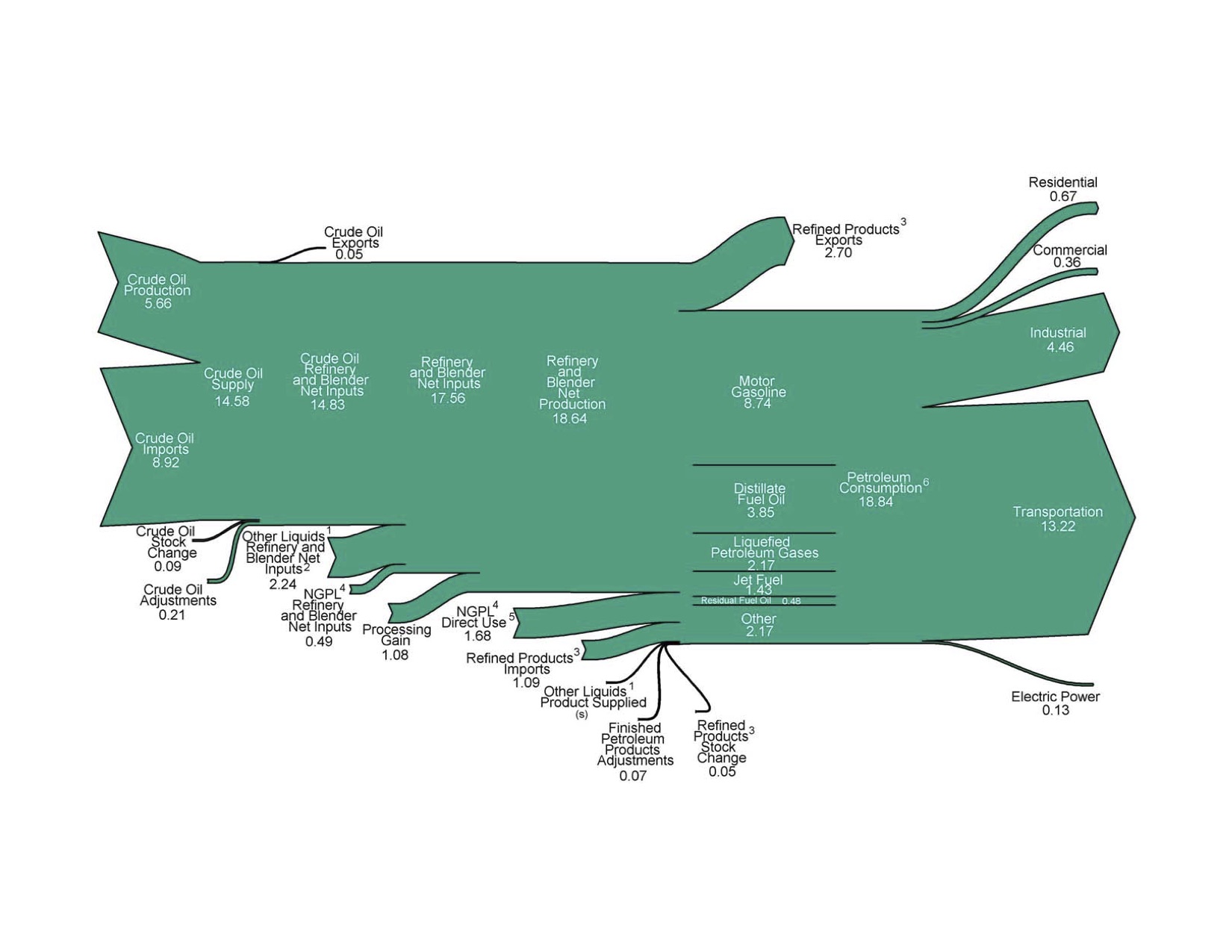
Petroleum prices
Certain prices are indexed and recorded
Petroleum use
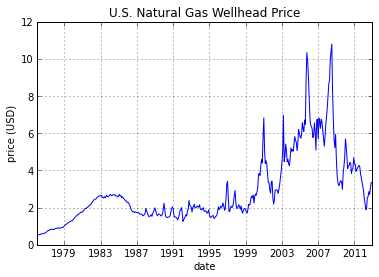
Natural gas prices currently low
Pollution effects
- Carbon dioxide climate
- Particulates
- Acid rain
Fossil Fuel Accidents
- Exxon Valdez 1989 Prince William Sound, Alaska
- Deepwater Horizon explosion 2010
- Sago Mine 2006 disaster
Related Videos
Reserves / Resources
- Resources:
- Proven reserves: lowest cost and lowest uncertainty
Refining
- Lighter molecules rise to the top of distillation towers