Solar Energy
Types of solar energy
- Solar Thermal
- Radiant energy to heat
- Very similar to a coal electricity plant
- Solar Photovoltaic
- Radiant energy directly to electricity using semiconductor technology
- Solar can be scaled from large to small amounts of generation
The journey of a photon
- Created in the core of the sun by nuclear fusion reaction
- Millions of years to bounce out to surface of sun
- Zips to earth in about 8 minutes
- Passes through the atmosphere
- Strikes a solar panel and dislodges an electron in the PV panel
- Electron is collected and delivered to the grid
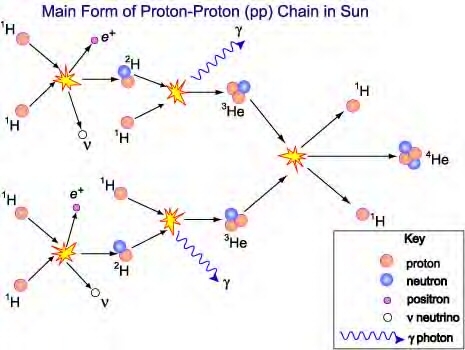
Solar radiation
- Conversion of mass energy to radiation
- Converts hydrogen to helium
Solar radiation
Solar energy
- Peak solar power about 1000 watts per square meter
- Solar power is usually measured for this level of sunlight
- However, sun is not always this bright
- Our sunniest locations get about 5.5 kWh per square meter per day of sun energy
Electromagnetic Spectrum
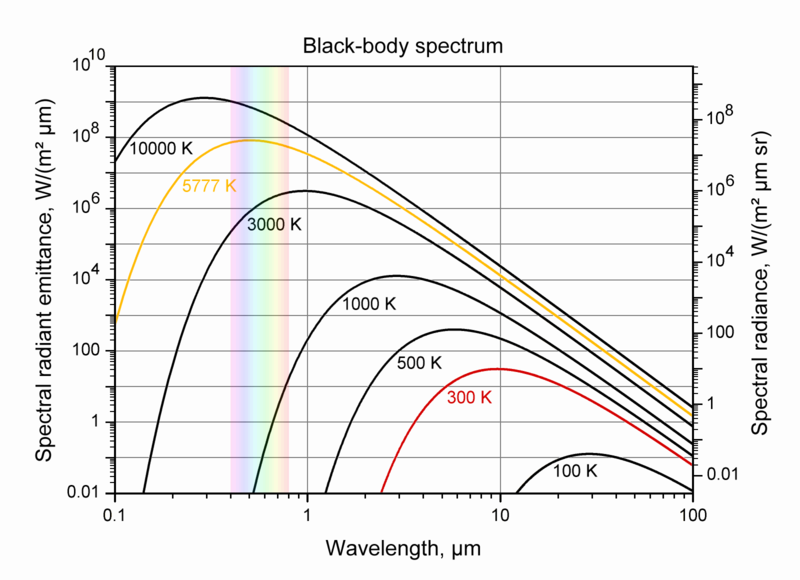
Blackbody Spectrum
Solar Photovoltaic
- Converts sunlight directly to electricity
- Commercially available panels have 15% – 20% efficiency of solar energy in to electrical energy out
Photovoltaic electricity plants
Agua Caliente
- Highest power photovoltaic power facility in 2013
- Yuma, Arizona
- 397 MW peak production
- 25 year power purchase agreement
Agua Caliente Data
Agua Caliente Monthly Production Data
Solar thermal plants
Parabola
A parabola is the shape that reflects parallel lines to a point. Since the sun’s rays are essentially parallel, this focuses the sun to a point.
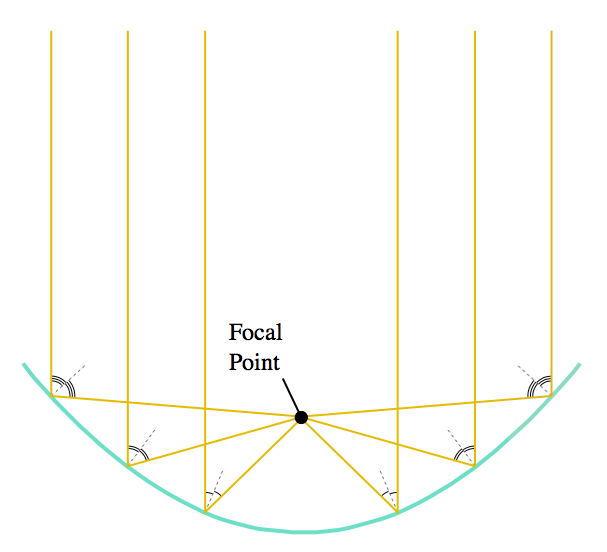
Concentrating solar power trough
We heat oil along large parabolic mirrors.
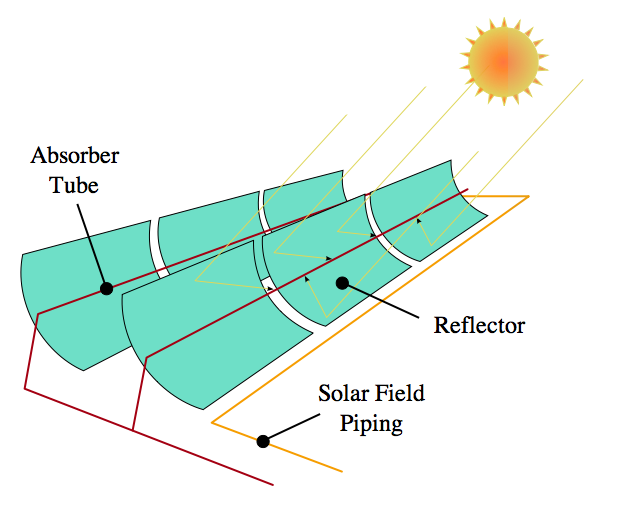
SEGS
- Solar Energy Generating Systems
- First solar thermal plants
- Daggett, CA
- Built in 1984 and 1985
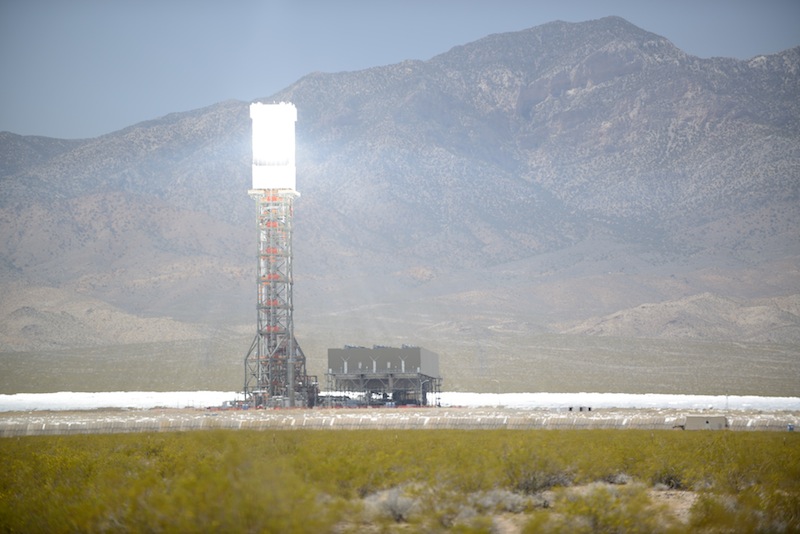
Ivanpah
- 377 MW
- Concentrating solar thermal power towers
- Near Las Vegas, Nevada
- No thermal storage
- Natural gas backup
Ivanpah solar plant

Solar power tower
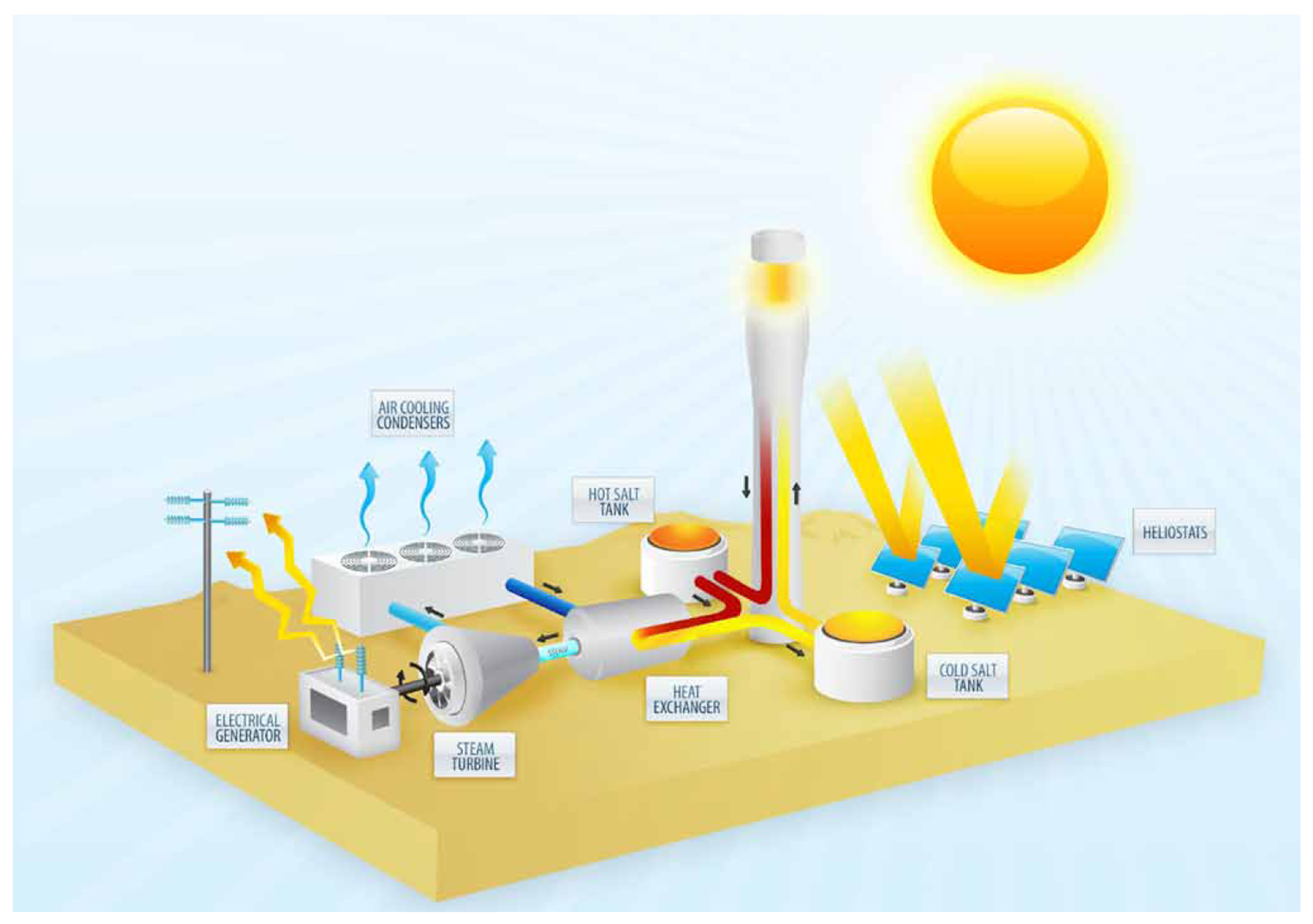
Solar Thermal
Advantages
- Uses well established thermal electricity technology
Disadvantages
- Needs water, scarce in sunny climates
Developing world solar
- Phone charging
- Water pumping
- Lighting
Solar Lantern

Solar Installed Capacity
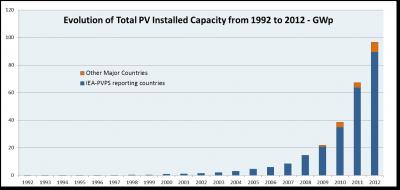
What scale is needed?
- World primary energy consumption approximately 500 EJ
- Power = Energy / Time
- Joules / seconds = Watts
Photovoltaic learning curve
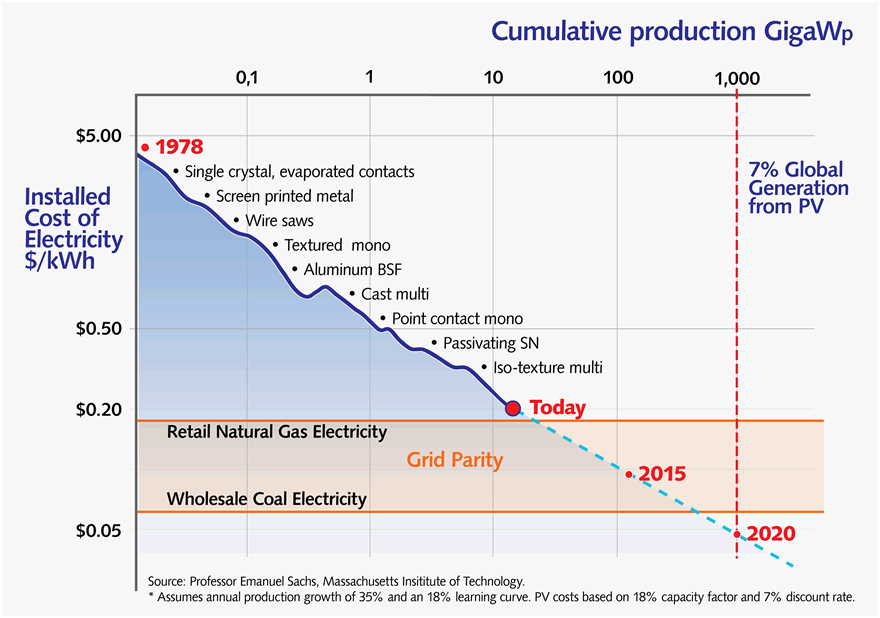
Solar Energy
- Approximately 1000 watts per square meter on the surface of the earth at peak
- 170 watts per square meter average insolation