Coal
Coal deposits formed about 300 million years ago (Carboniferous era) from plant matter. Under pressure and temperature, the plant matter becomes carbon-rich. This process is very similar to pyrolysis.
The energy in these deposits was originally from photosynthesis, using carbon dioxide and water to create hydrocarbons.
This energy is released by combustion.
Coal Use
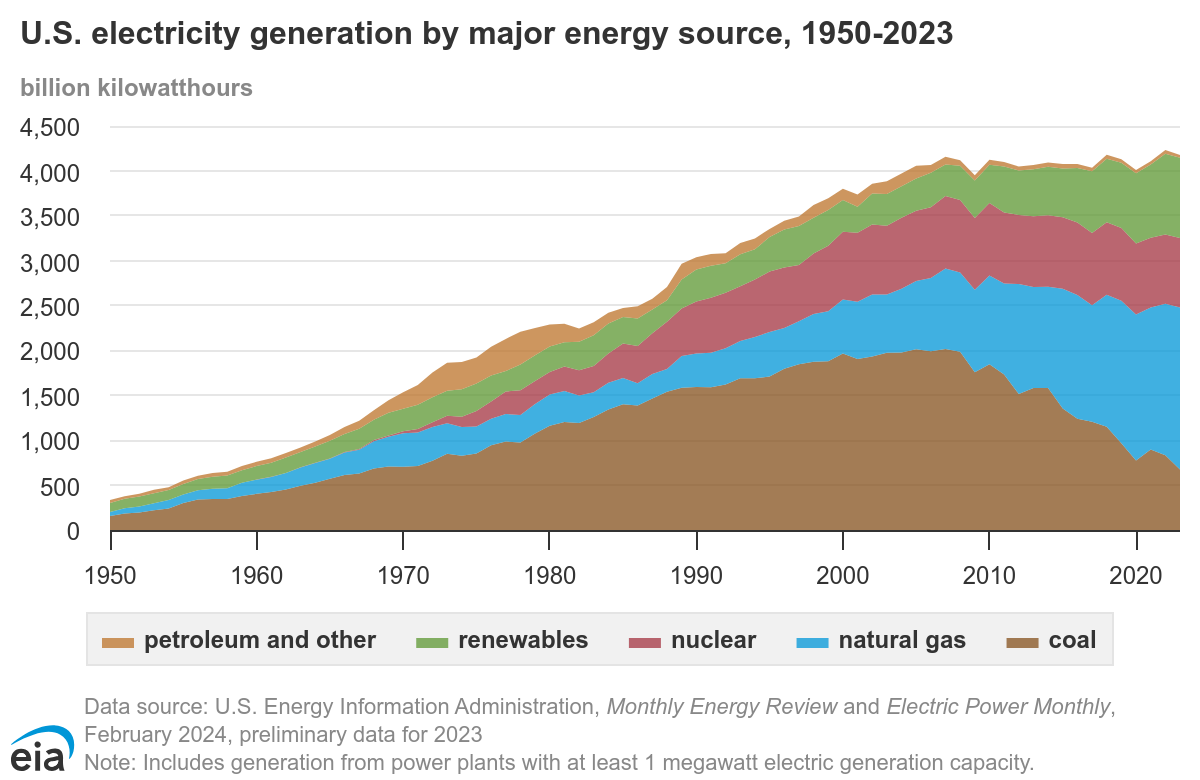
Steam Electricity Generation
Coal, a primary energy source is converted to the secondary energy source of electricity.
This thermal to mechanical conversion based on steam is called the Rankine cycle. Similar conversions are found in nuclear, natural gas, geothermal, and solar thermal electricity generation
Stakeholders
- Mine laborers
- Mine owners
- Coal electricity plant owners
- Electric Utilities
Techno-economic Perspectives
Coal-fired electricity diagram
Environmental Perspectives
Coal has several environmental effects
- GHG emissions from combustion
- Toxic releases from sulfur, mercury, and other chemicals
- Surface mines create debris issues
- Ash storage has spilled
Total Mercury Emissions over time
Socio-Technical
The workforce associated with coal has dropped from 178 thousand persons in the late 1980s to about 41 thousands persons in 2025.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics data