Petroleum
Formation
- Fossil fuels are the product of millions of years of photosynthesis stored and processed under heat and pressure
- Most fuel is found in rocks from about 50-450 million years ago
- Limestone, sandstone, and shale
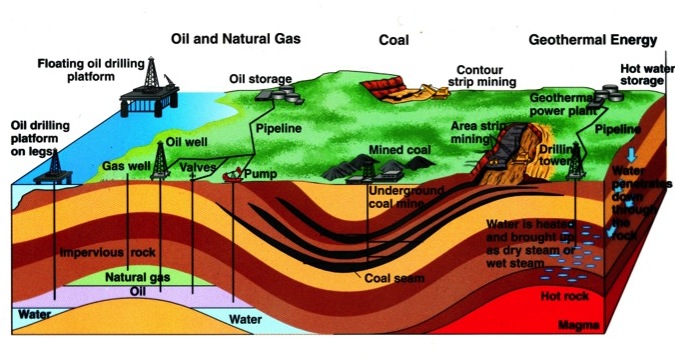
Petroleum/ Crude Oil
This is a primary source that is liquid hydrocarbons found in rock deposits.
Natural Gas
This is a primary source that is gaseous hydrocarbons found in rock deposits, sometimes together with liquid oil, sometimes without.
Light/Heavy
Light crude oil has smaller molecules on average and heavy crude oil has larger ones.
Sweet/Sour
Sweet crude oil is less than 1% sulfur, while sour crude oil is around 1-2% sulfur.
Gasoline
Gasoline is a secondary energy source created from crude oil in refineries.
- Lighter molecules rise to the top of distillation towers
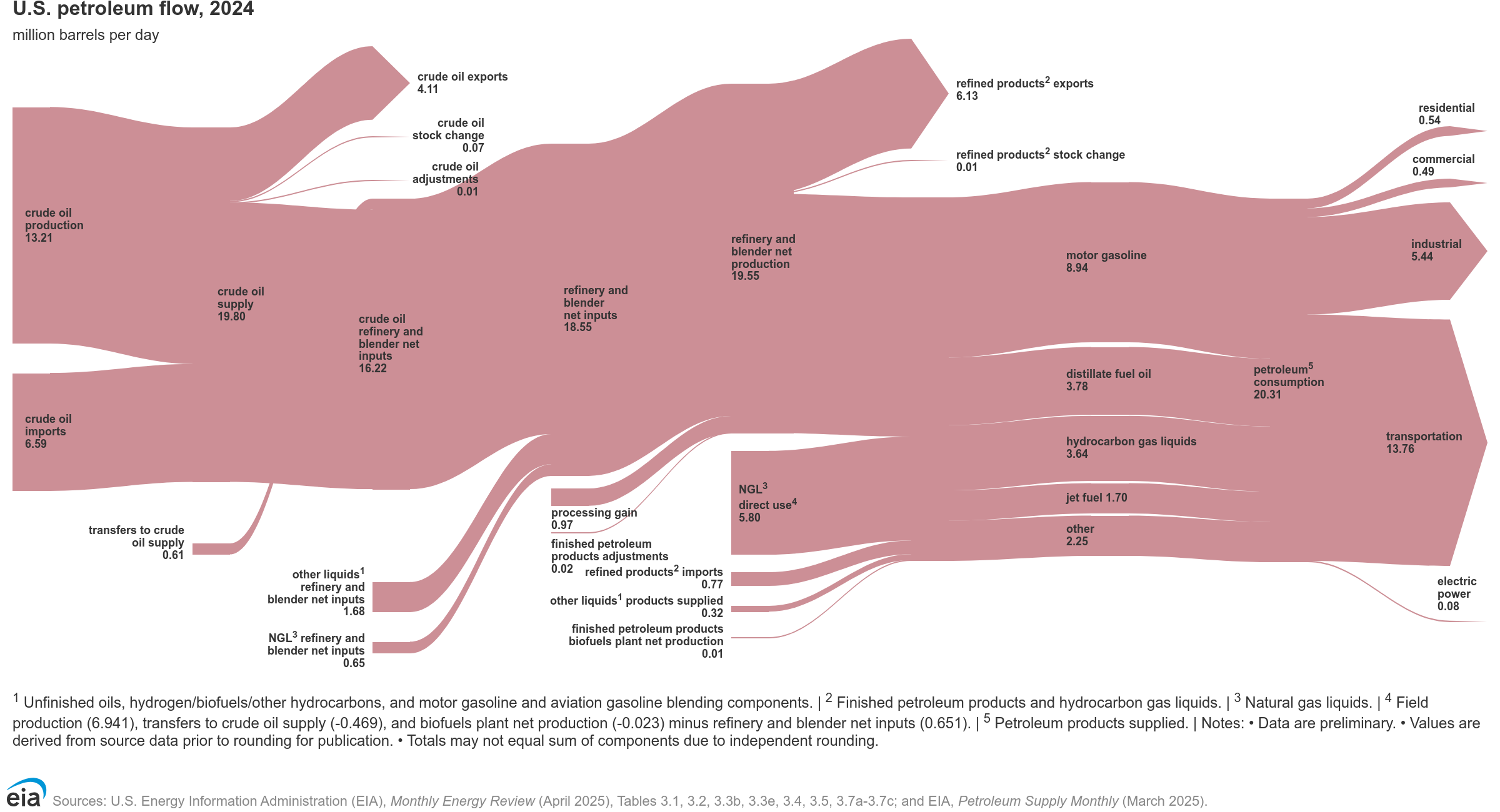
Flows

Stakeholders
- Oil field labor
- Oil field owners
- Refinery labor
- Refinery owners
- Automobile drivers
- Political leaders
Techno-economic perspectives
- Hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling
- Internal combustion engine
- Oil has high energy density
- Oil is easily stored and transported
- Natural gas is liquified for overseas export
Internal Combustion Engines
- Combustion: Gasoline and Oxygen
- Expansion: Combustion gasses expand
- Linear Kinetic Energy: pushes on piston
- Rotational Kinetic Energy: piston pushes on crankshaft
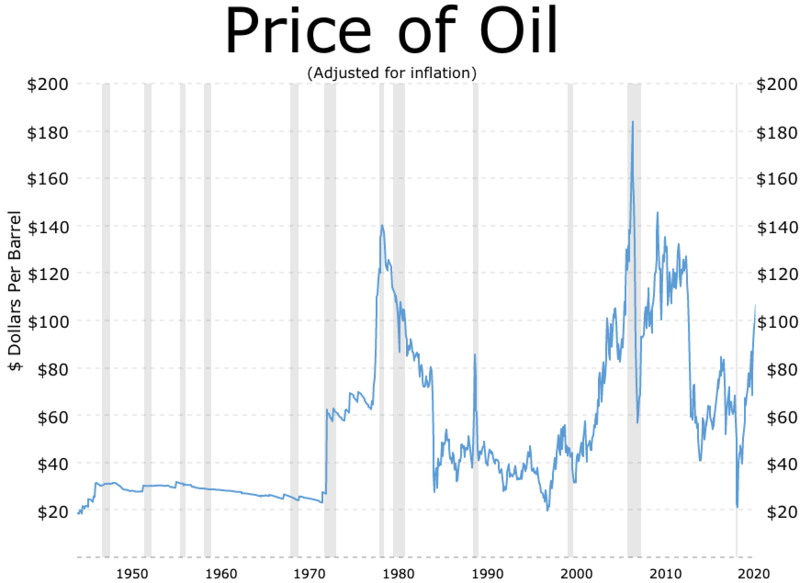
Prices
Environmental Perspectives
- Lead/MTBE
- Tailpipe Emissions
- Storage spills
- Oil spills
- Exxon Valdez 1989 Prince William Sound, Alaska
- Deepwater Horizon explosion 2010
- GHG gases
Socio-Technical perspectives
- Jobs Data
- Geopolitical conflicts
- Resource curse
Policy
- Crude export ban 1975 Energy Policy and Conservation Act
- Ban lifted in 2015
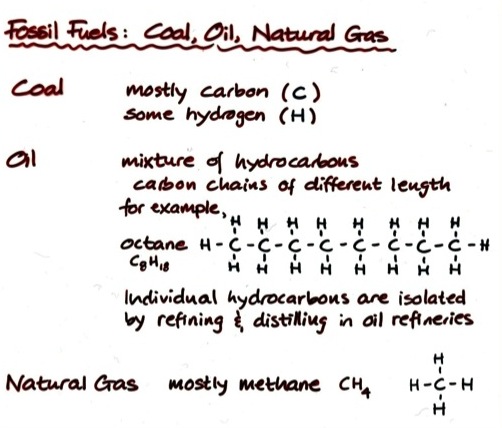
Fossil Fuel Molecules

Petroleum prices
Certain prices are indexed and recorded