Wind Power
Wind map
Energy Source
Primary energy source is kinetic energy of air molecules.
The most common secondary energy source is electricity.
Energy Conversion Processes
- Solar radiation heats land and air
- Expanding air creates kinetic energy in wind
- Wind kinetic energy transfers to turbine kinetic energy
- Converts kinetic energy to electrical energy using a generator
Similarities to Rankine cycle
- Spinning electromagnetic generators
- Sun is heat source
- Moving air but not steam
Vestas Website
Techno-economic Perspectives
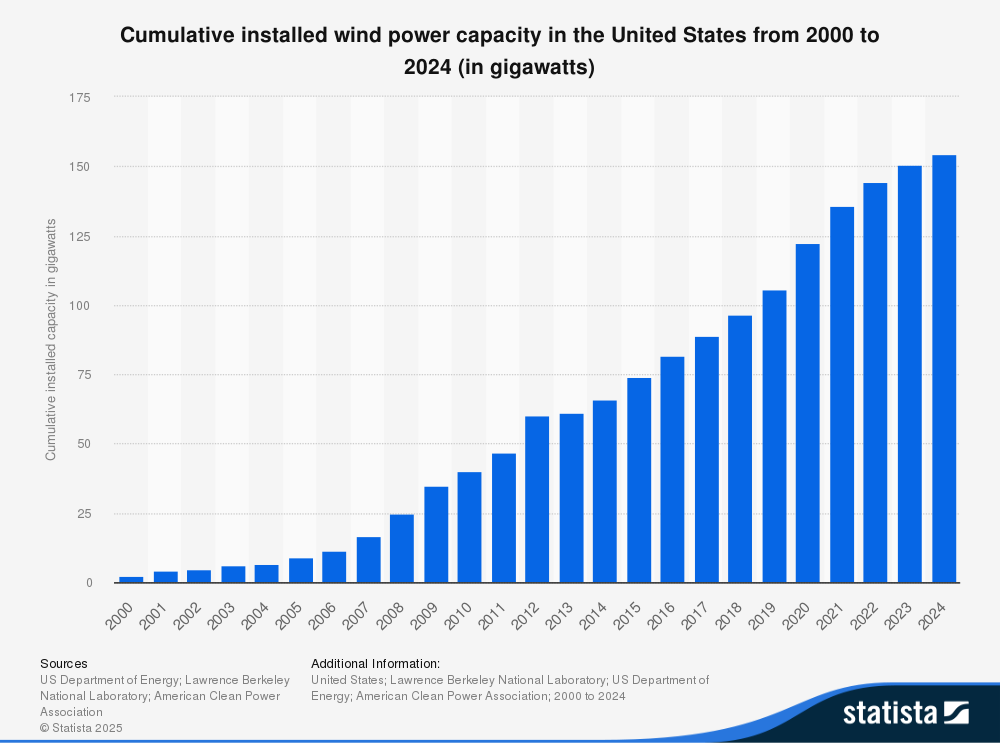
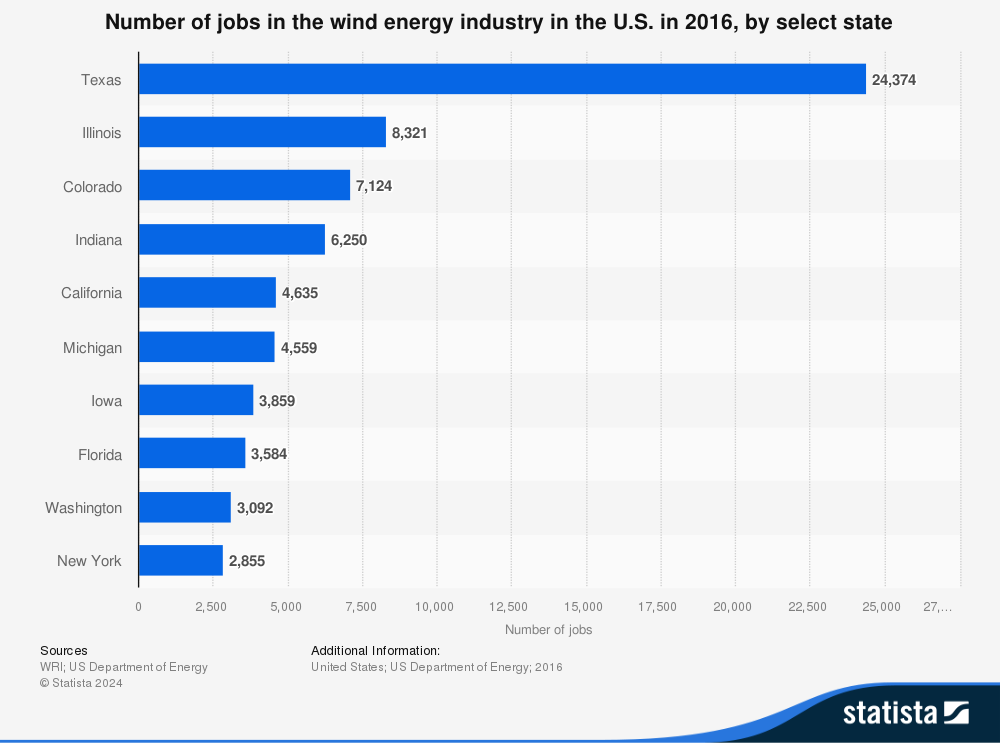
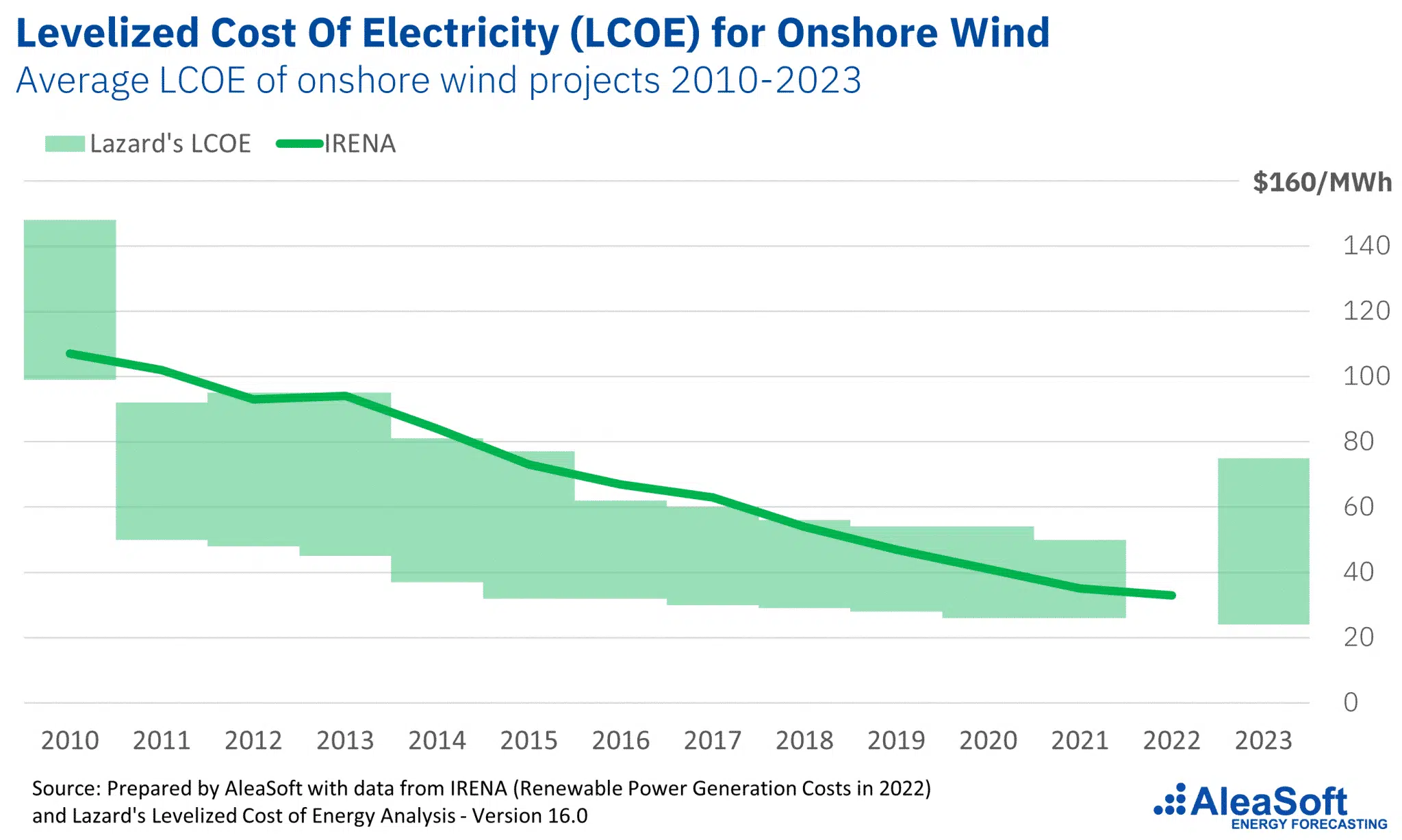
Environmental Perspectives
Environmental and Ecological Impacts
- Low carbon emissions (only during manufacture and installation)
- No significant water impact
- Hazardous to birds, bats, and raptors
Socio-Technical
- Construction requires heavy machinery
- Land owners often want freedom to use their land for energy
- Offshore wind potentially spoils the view from valuable properties
Policy
- Migratory Bird Treaty Act (MBTA) prohibits inadvertent/unintentional bird deaths
- Windmill operators can get permits for bird deaths if they have mitigation plans
- A recent executive order would remove unintentional bird deaths from the MBTA