Solar Energy
Solar Energy
Primary energy source of radiation from fusion reaction in the Sun.
Solar photovoltaics convert solar radiation to electricity, a secondary energy source.
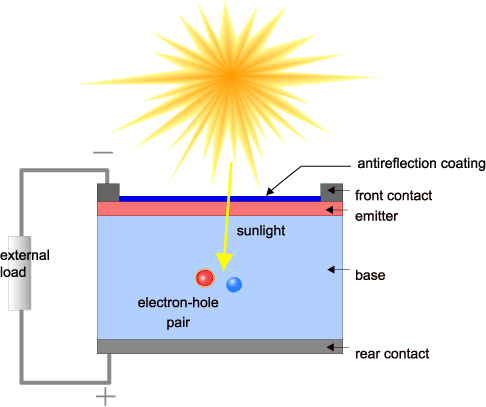
Solar Photovoltaic
- Converts sunlight directly to electricity
- Commercially available panels have 15% – 20% efficiency of solar energy in to electrical energy out
Photovoltaic electricity plants
Agua Caliente
- Highest power photovoltaic power facility in 2013
- Yuma, Arizona
- 397 MW peak production
- 25 year power purchase agreement
- Map Link
What scale is needed?
- World primary energy consumption approximately 500 EJ
- Power = Energy / Time
- Joules / seconds = Watts P = 500 EJ / 3.15 \cdot 10^{7}\ seconds = 16 TW
Solar Energy
- Approximately 1000 watts per square meter on the surface of the earth at peak
- 170 watts per square meter average insolation
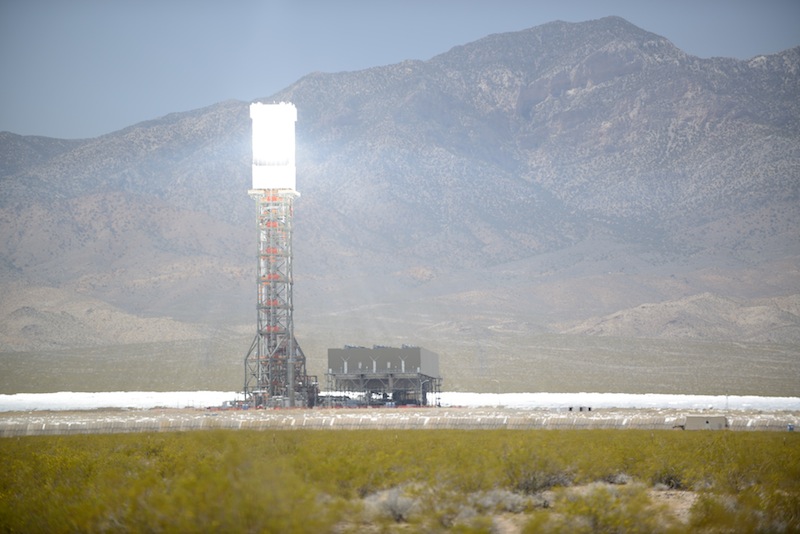
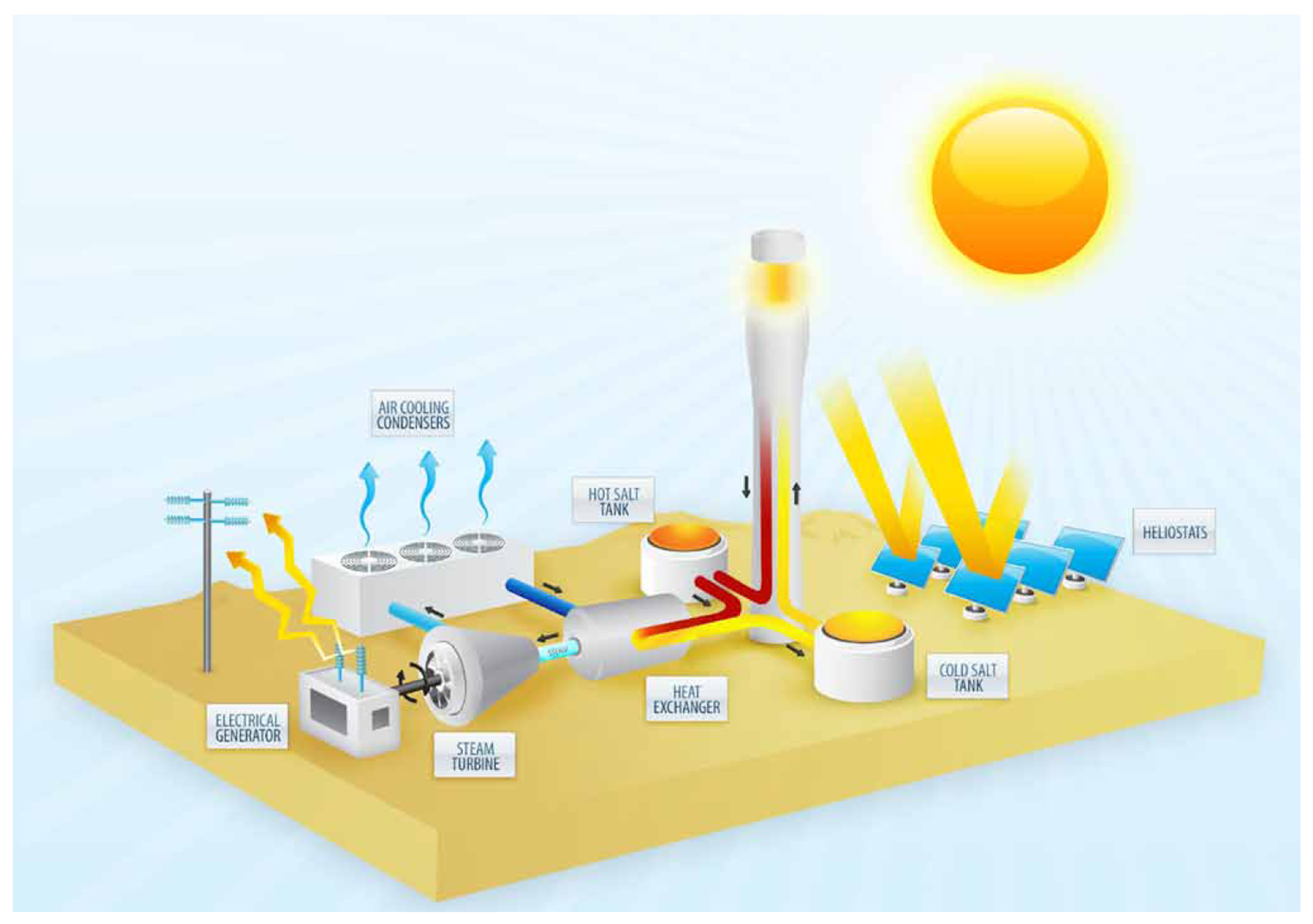
Solar thermal plants
Use solar radiation converted to heat to create steam to spin a turbine.
Not yet commercially viable.
Ivanpah solar thermal plant

Solar power tower
Stakeholders
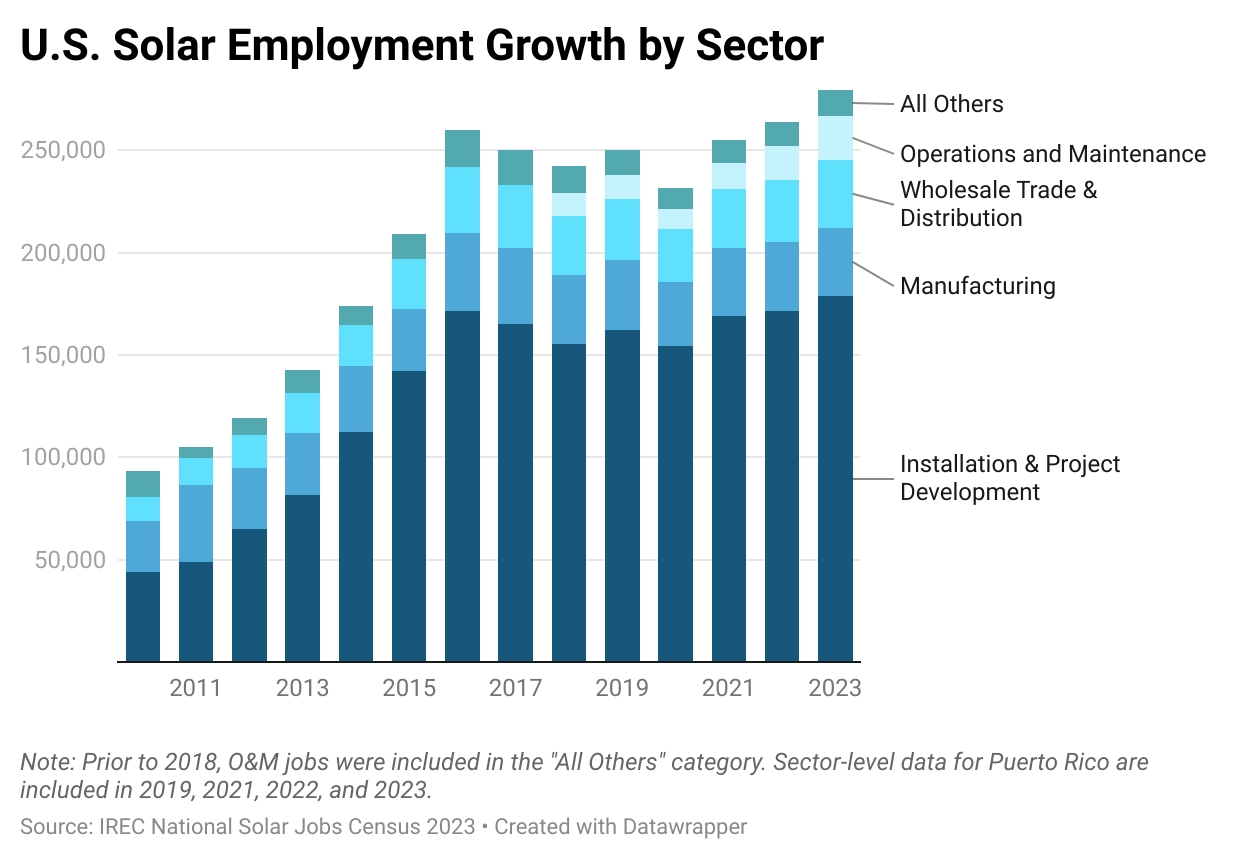
- Solar labor
- Solar manufacturers
- Solar installation companies
- Grid operators
- Competing electricity providers
Environmental Perspectives
- No carbon emission or pollution during operation
- Manufacturing uses hazardous chemicals
- Large land footprint and ecological changes
- Will eventually generate waste streams
Techno-economic Perspectives
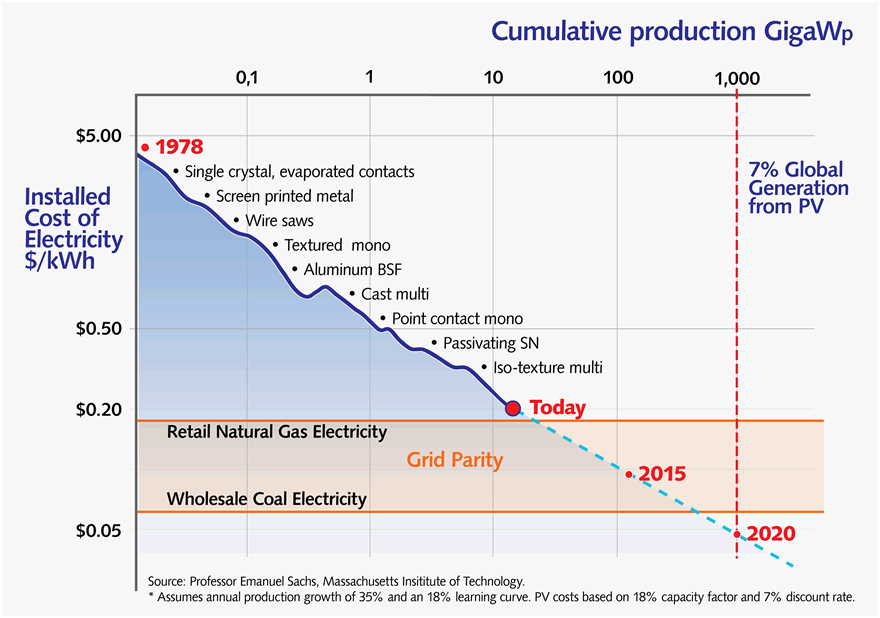
Photovoltaic learning curve
Solar becomes cheaper as we build more of it.
Socio-Technical Perspectives
- Solar is likely the largest end-user owned source of electricity generation
- Popular among homesteaders
- Is deployed in both blue and red states
Policy
- IRA created tax credits for clean energy that included solar
- OB3 ends these credits before the IRA end date