The Linear Function as a Tool
If a linear model is appropriate for the situation we are trying to analyze, there are several mathematical techniques that may be of interest.
- Extrapolation
- Interpolation
- Regression or Fitting
Extrapolation
Extrapolation is the use of a linear model to make a prediction. Usually, our linear model is valid over a certain range. In an extrapolation, we assume the model is valid beyond that range and ask what our model would predict.
There are two approaches to extrapolation
- doing a calculation based on the slope and an existing data point
- using a ruler or other visual aid on a graph to estimate
Interpolation
Interpolation is the use of a linear model to make a prediction. If we have data on both sides of our region of interest, we can make predictions in between.
Linear Fits or Regression
- If we have a bunch of data that is roughly linear, we can use a linear function as a model
- The process of finding this linear model from the data is called regression or fitting
Linear Extrapolation
- If we assume a relationship, we can predict its value in the future
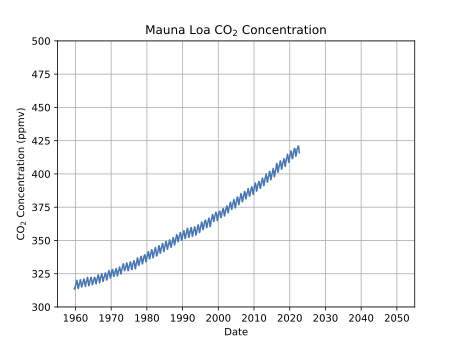
Extrapolation Formula
It is helpful to be able to see how the pieces of the extrapolation formula correspond to a visual picture.
- Find the slope of the known portion of the graph so you have the relationship between x and y.
- You are calculating the distance on the x-axis between your last known data and the point you want to compute. This will be the run in a slope triangle.
- Multiplying this x-distance by the slope will give you the rise in a slope triangle.
- Adding this to the last known y-value will give you the corresponding value of y for the x you chose.
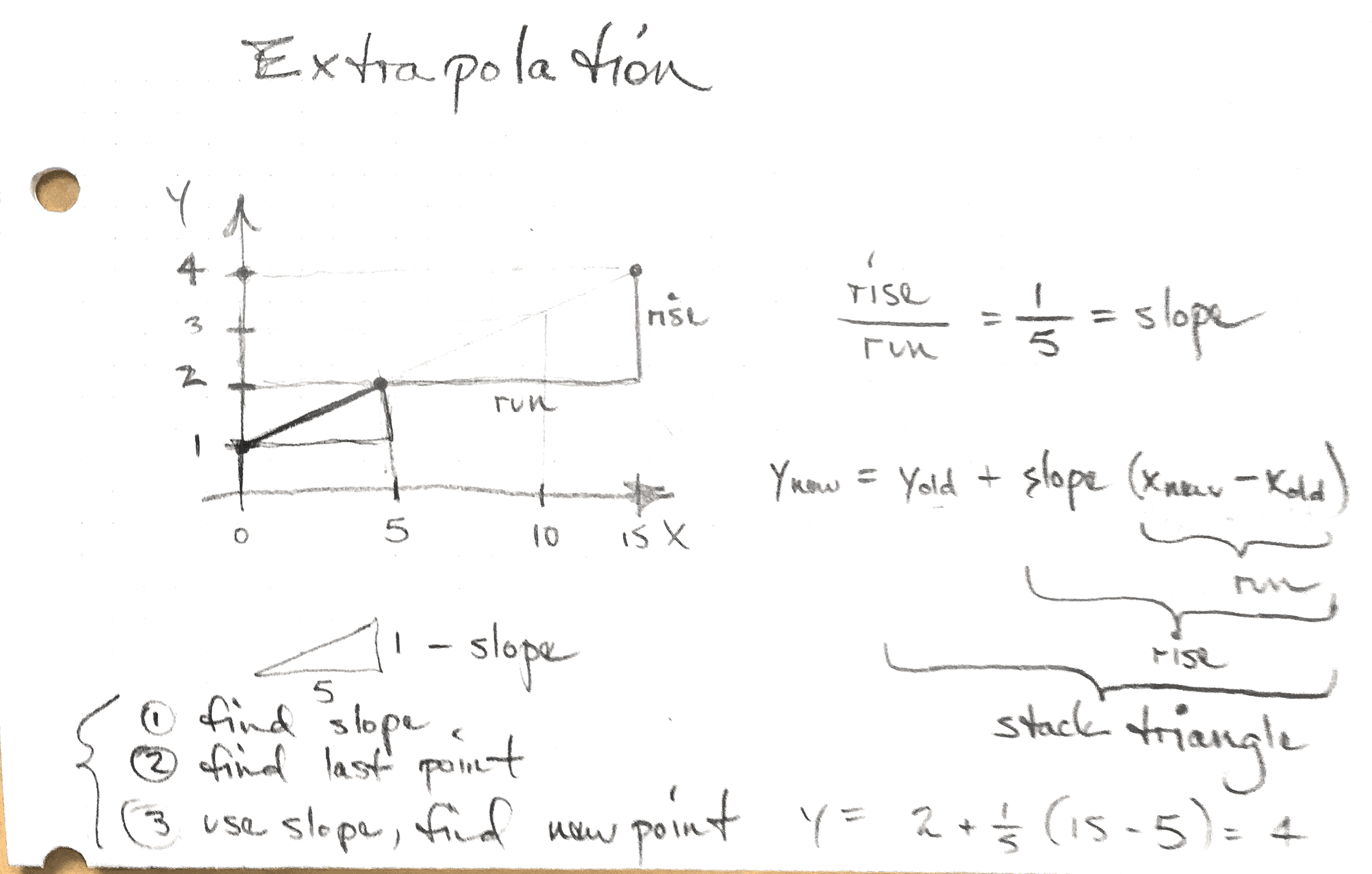
Mauna Loa Data