Electrical safety
Electrical hazards
- Joule heating of human tissue
- Involuntary muscle contractions
- Ventricular Fibrillation
Resistance of Humans
- Ranges from 100\Omega to 1M\Omega
- Equivalent circuits for humans
Heart stoppage
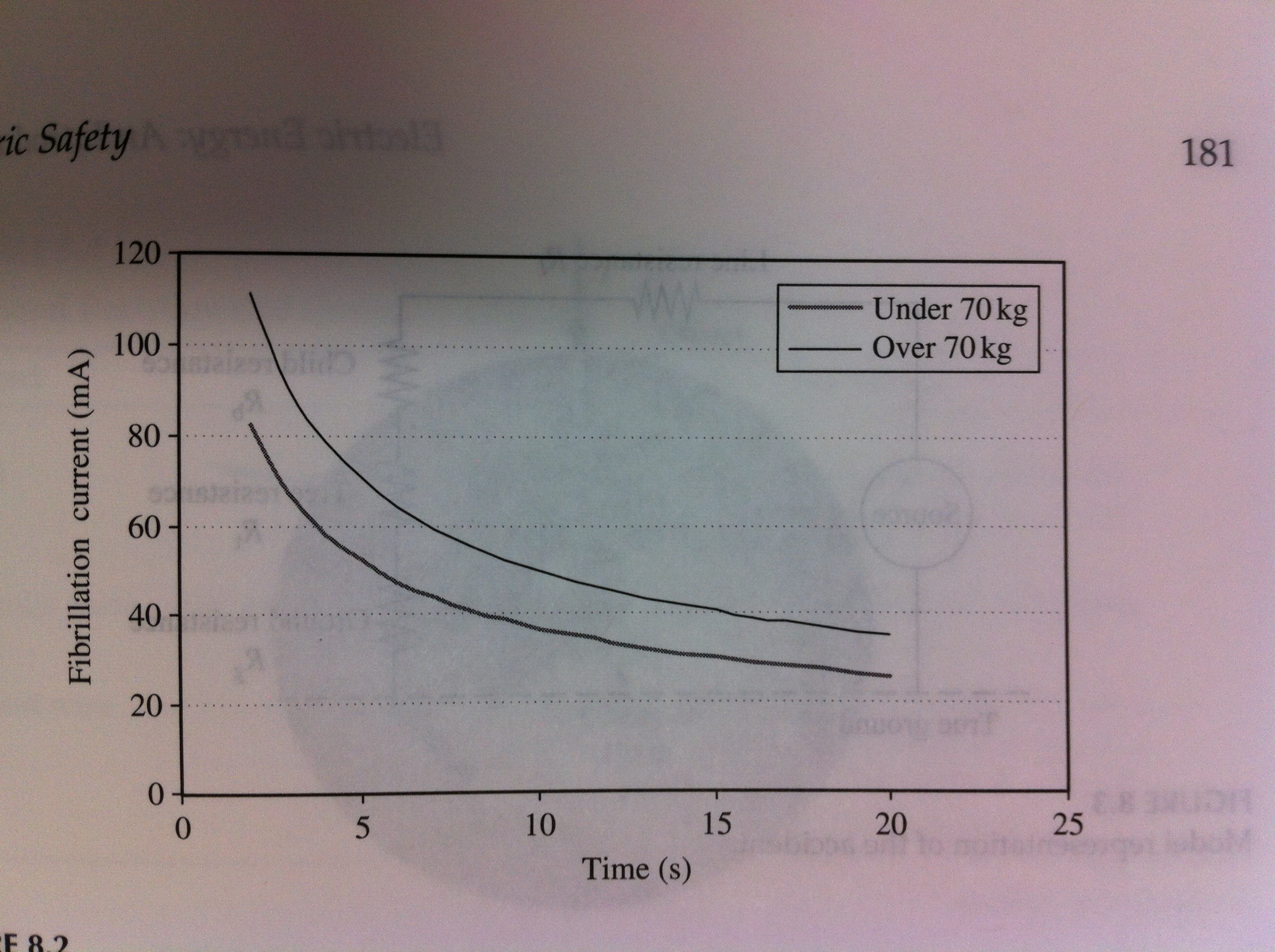
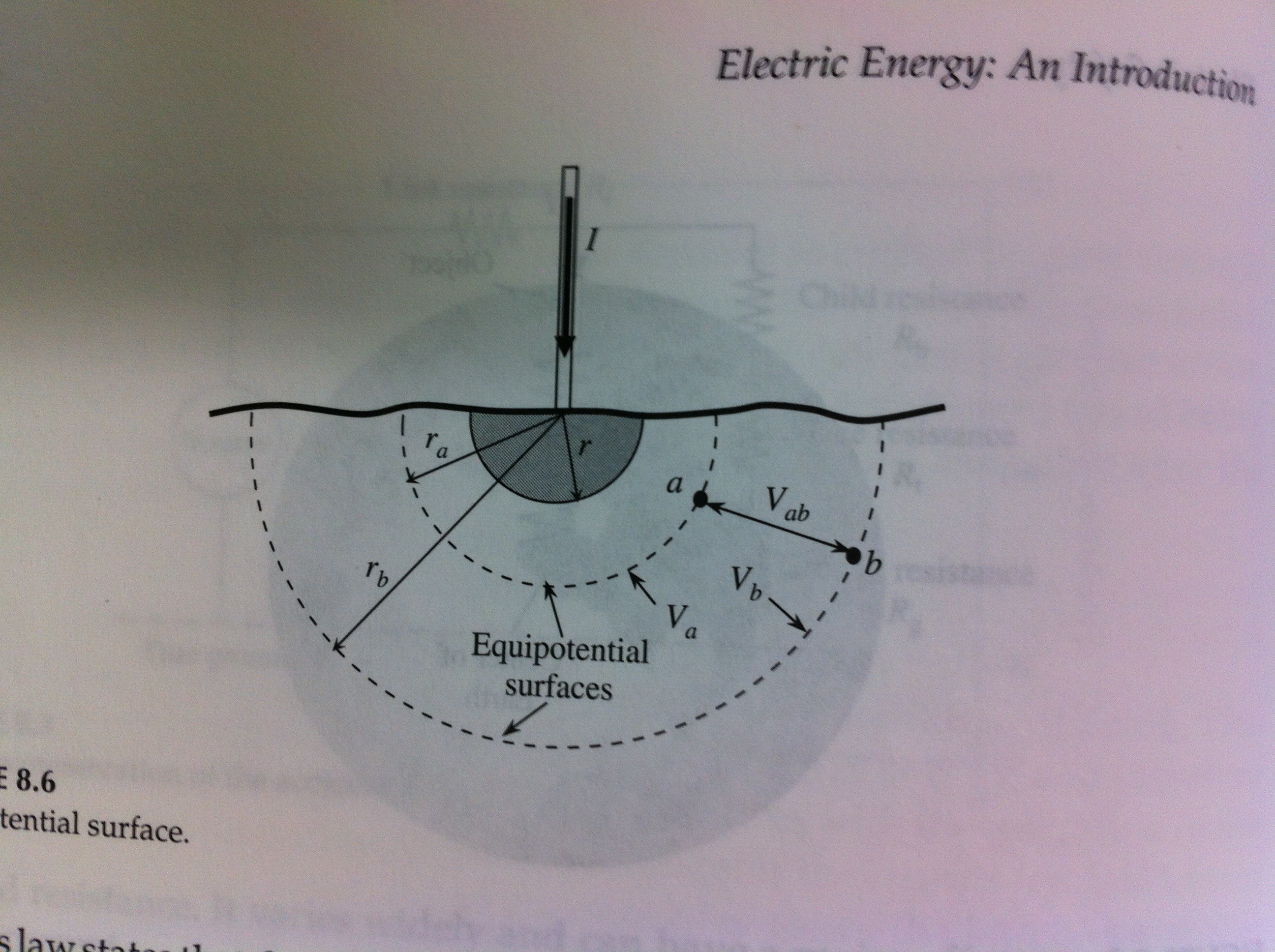
Step potentials
- Large currents flowing to ground can create hazardous voltage differences along the ground
- If the potential difference across a persons stride is high enough, a shock can occur
Step potentials
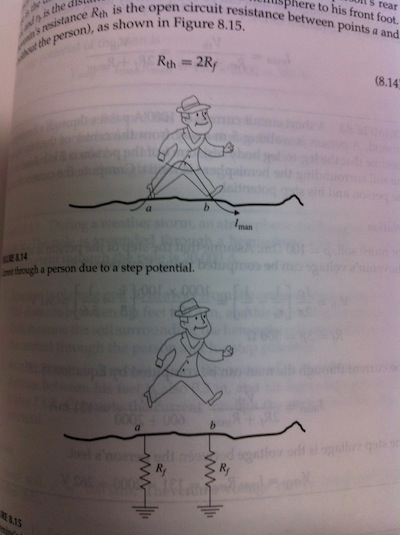
Step potentials
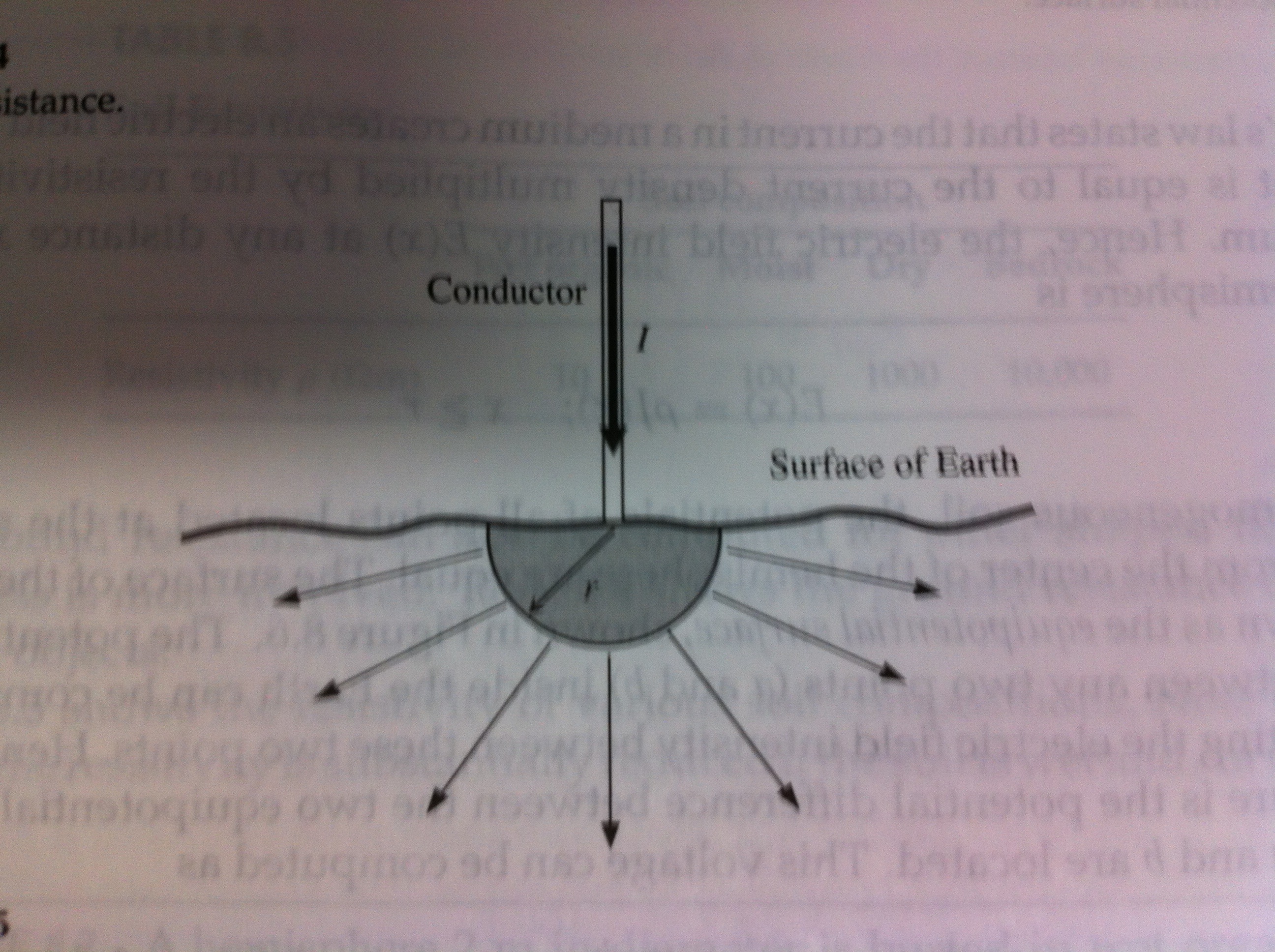
Step potentials
Ground Fault Circuit Interruptor (GFCI)
- A ground fault circuit interruptor monitors the difference in current between the hot and neutral lines
- If the current is unequal, that means that another conductor is carrying current to ground, which is a hazardous situation.
- If Kirchoff’s current law is violated, something unsafe might be happening.
Ground Fault Circuit Interruptor (GFCI)

Ground Fault Circuit Interruptor (GFCI)