Temperature
Temperature
- Measure of the internal energy in a system or material
- This energy is the motion, vibration, or rotation of atoms and molecules
Interval and Ratio Data
Interval data is data where the differences between two measurements is meaningful. Fahrenheit and Celsius are both interval data.
Ratio data is data where both the differences and ratios between two measurements are meaningful. Kelvin (and Rankine) data are ratio data since the zero point represents the lowest possible temperature. Whenever you see a ratio equation (like second law efficiency), you must use a ratio temperature scale. Using an interval scale (F or C) will give incorrect results.
Temperature Scales

Converting Temperature
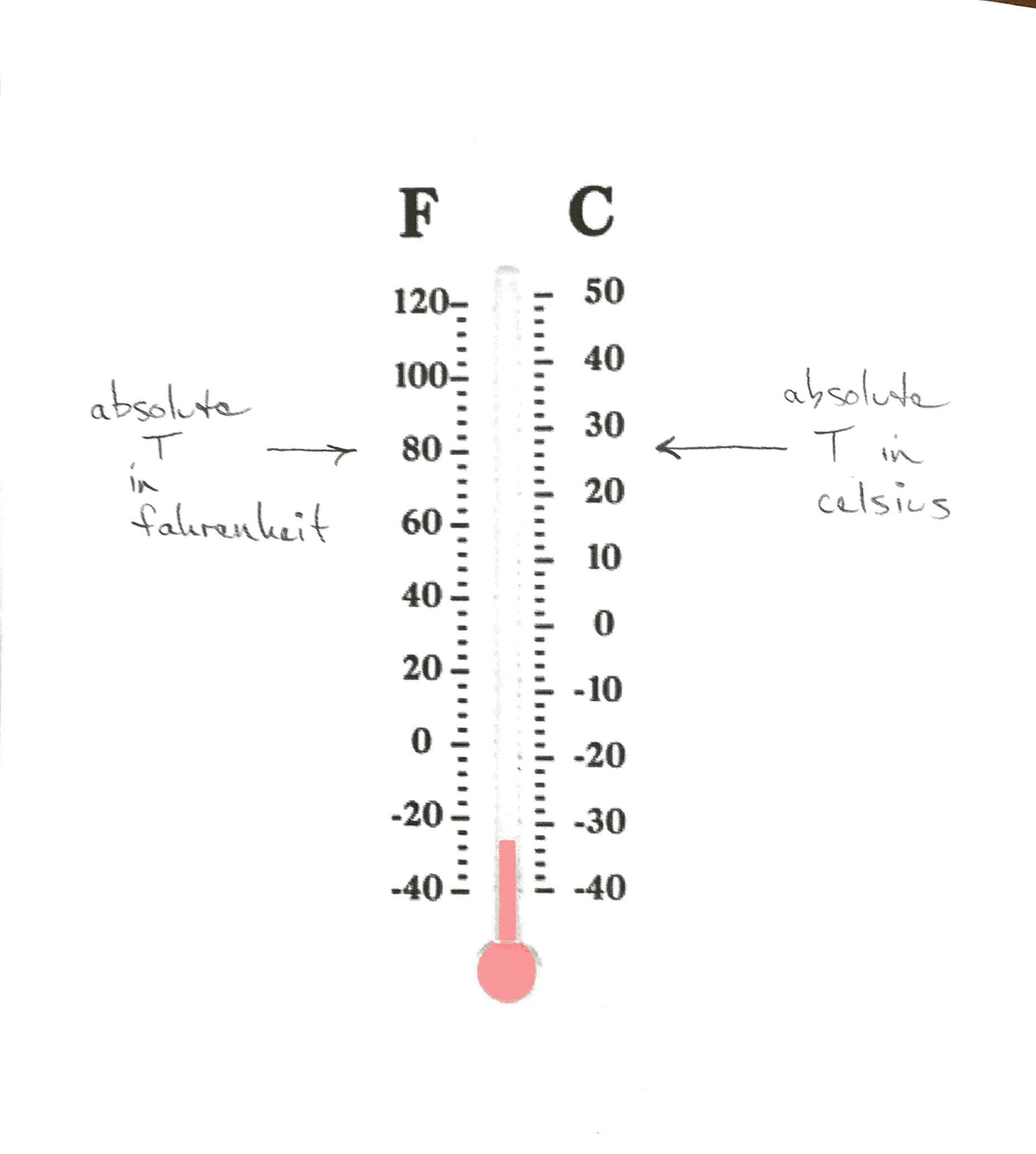
- Absolute temperature conversion
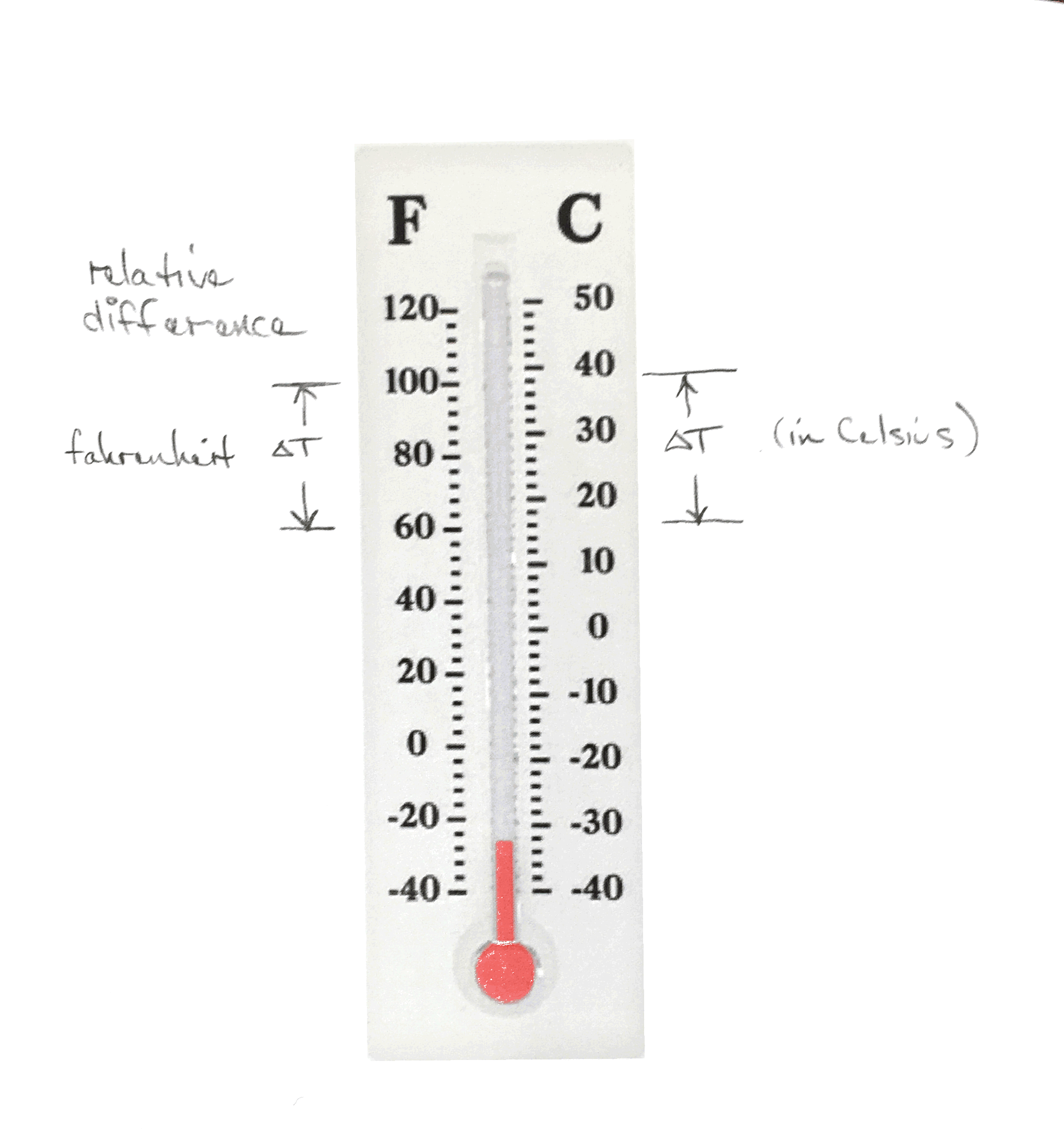
- Temperature difference conversion
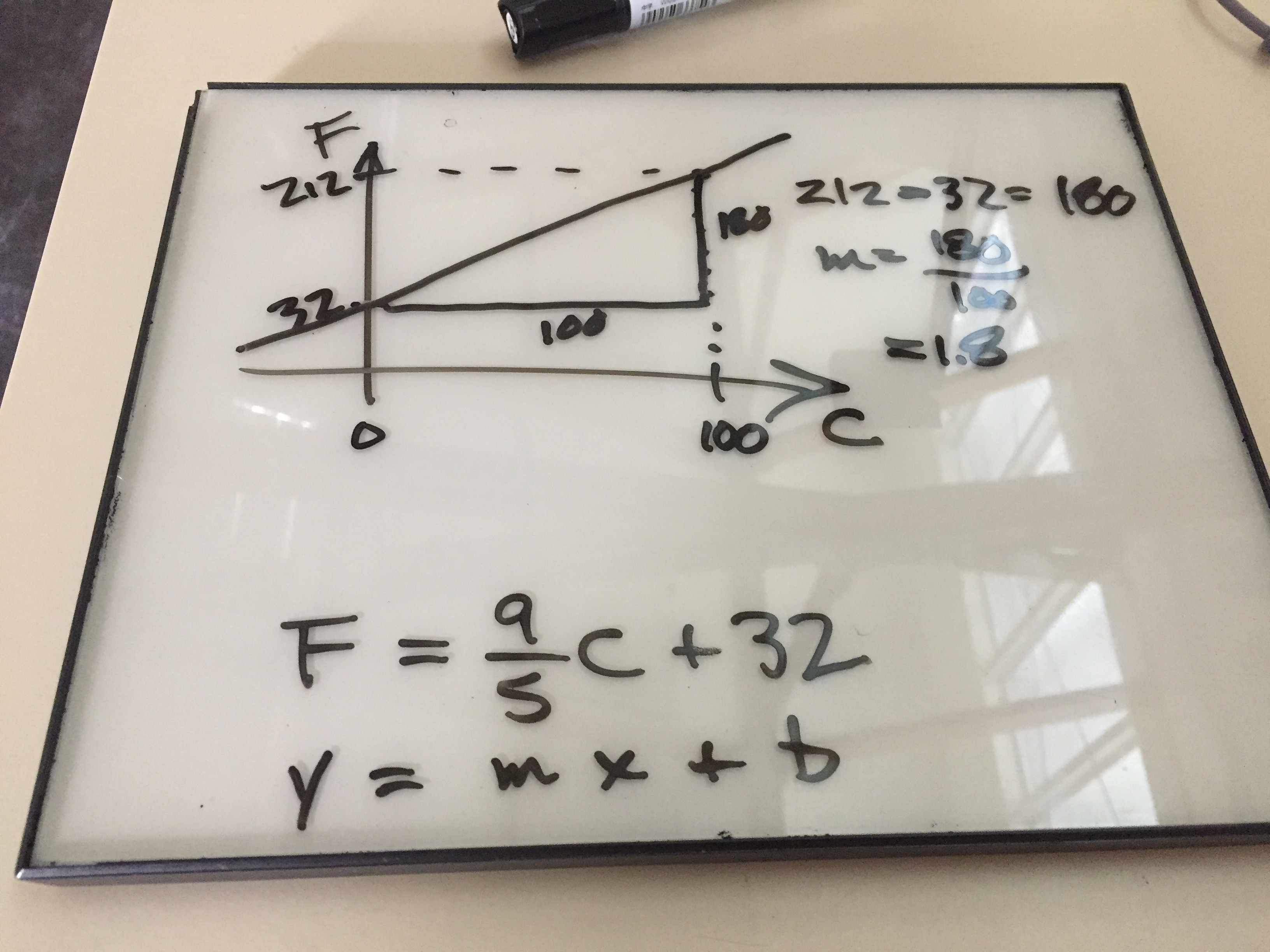
T_{F} = \frac{9}{5} T_{C} + 32
\Delta T_{F} = \frac{9 F}{5 C} \Delta T_{C}
T_{C} = \frac{5}{9}(T_F - 32)
Note that a degree C is a larger increment in temperature than a degree Fahrenheit. This makes it easier to deduce whether to multiply by 9/5 or by 5/9.
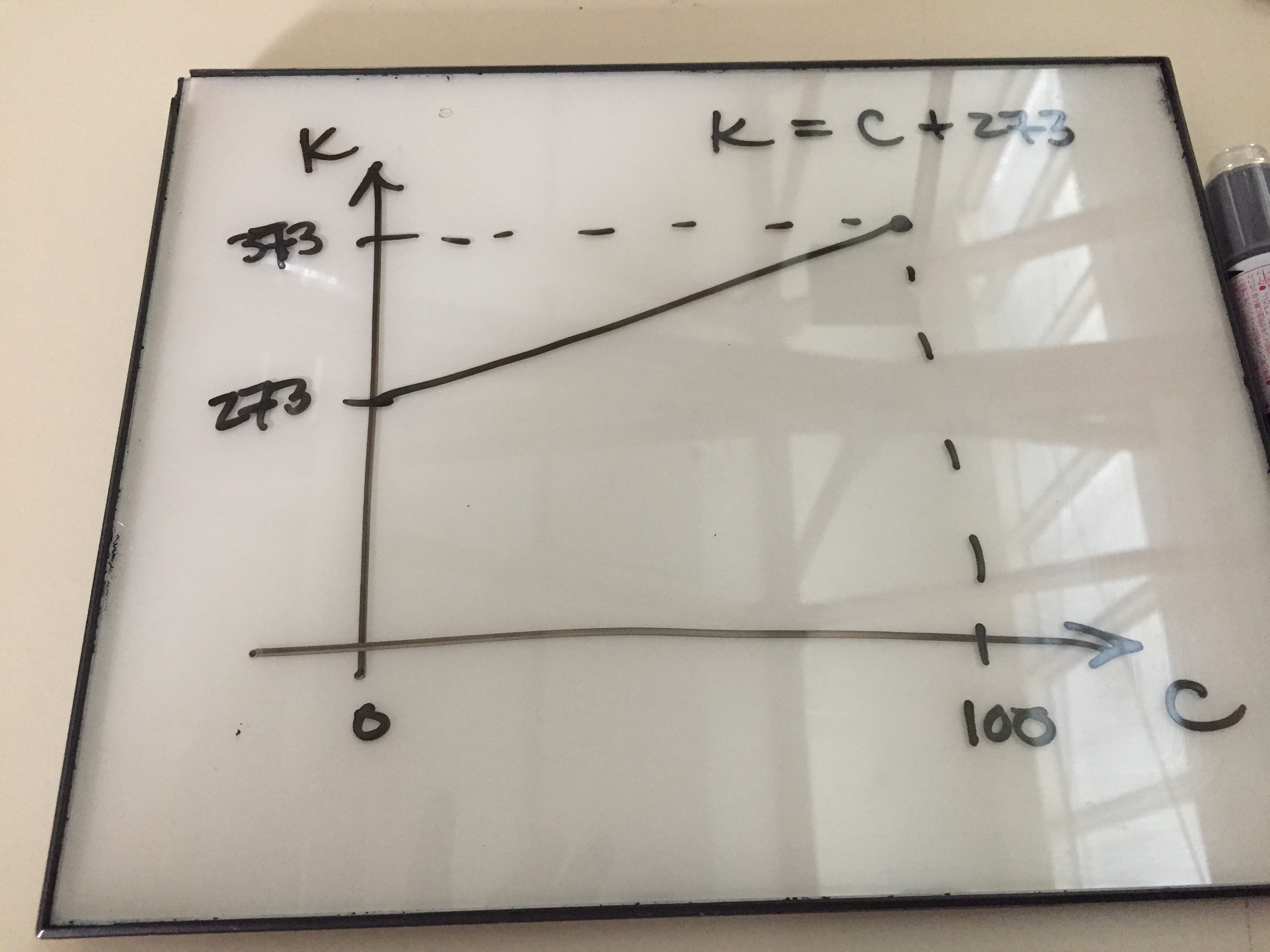
T_{K} = T_{C} + 273.15
T_{C} = T_{K} - 273.15