Solar Angles
This section covers the angles at which solar energy arrives to the surface.
From this we can determine how much energy is available over an area to be used for heat or electricity. From this knowledge we can place photovoltaic panels, building windows, or heat collectors correctly.
The journey of a photon
- Created in the core of the sun
- Millions of years to bounce out to surface of sun
- Zips to earth in about 8 minutes
- Passes through the atmosphere
- Strikes a solar panel and dislodges an electron in the PV panel
- Electron is collected and delivered to the grid
Electromagnetic Spectrum
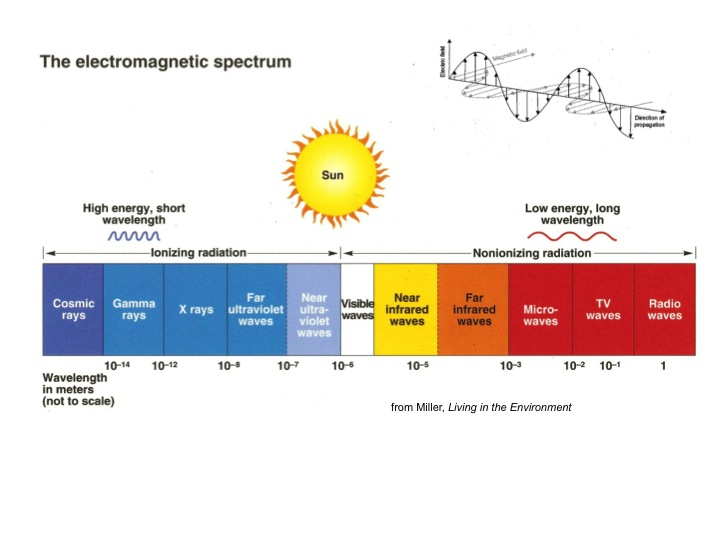
Blackbody Spectrum
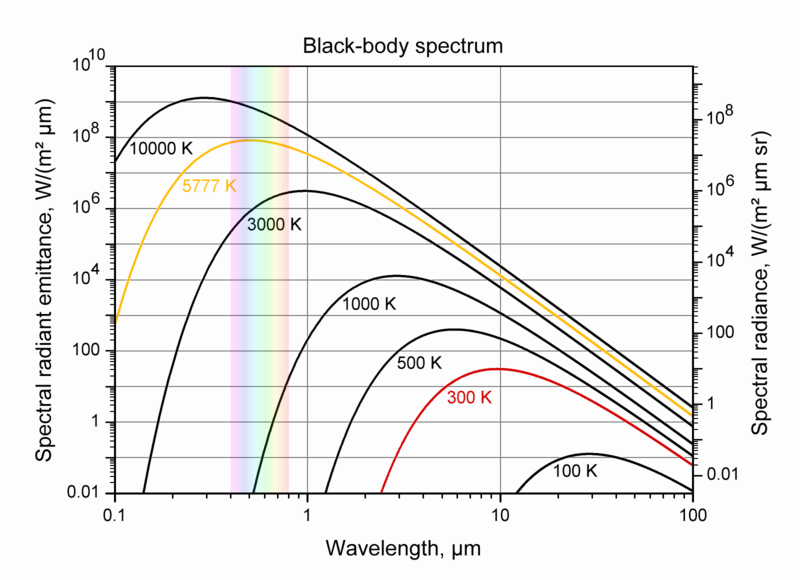
Solar Spectrum
The Solar System
Earth sun distance
d=1.5 \times 10^8 \left(1 + 0.017 sin\left(\frac{360(n-93)}{365}\right)\right)km
- n is the day of the year
- Is this close to circular?
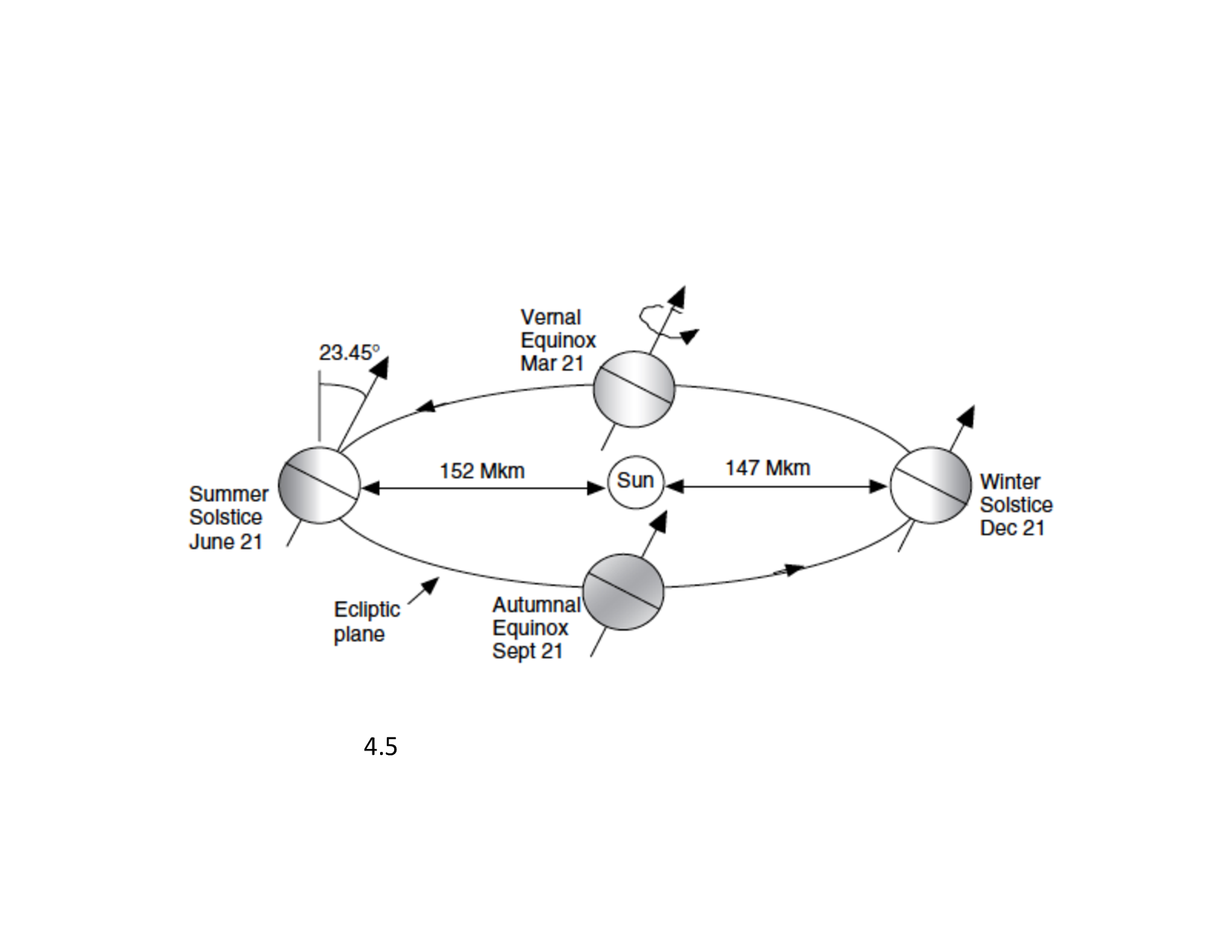
Earth orientation and orbit
Sun Ray Angles
- Declination: angle between equatorial plane and sun
- Elevation: angle between local surface of earth and sun angle
- Azimuth: angle between perpendicular north-south plane and sun angle
Sun Ray Angles
Sun Ray Angles
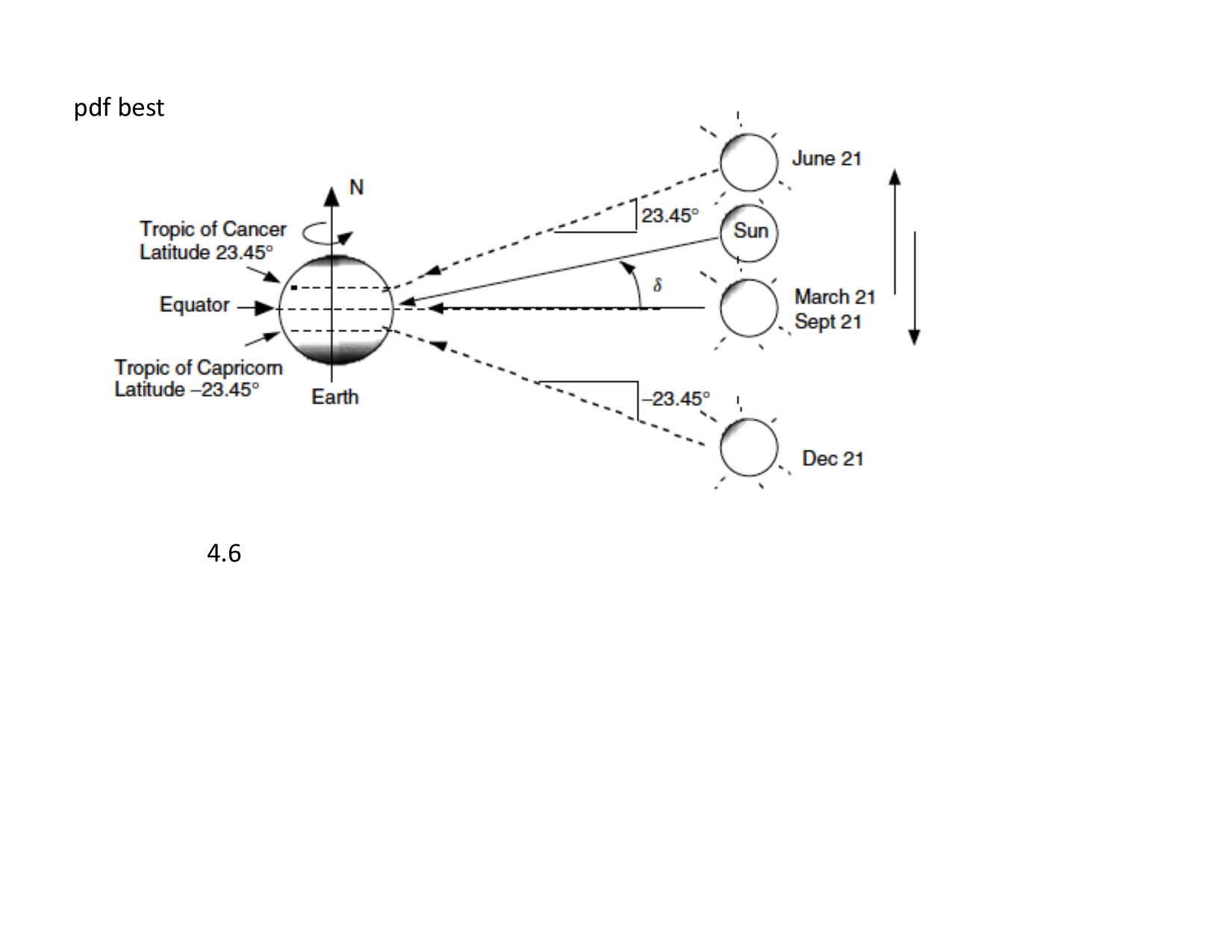
Solar declination
- Measures the elevation of the sun relative to the earth’s equitorial plane
- From the earth’s perspective, the sun exhibits a sinusoidal up and down motion with a period of one year.
Solar declination
Declination equation
We can estimate the declination of the sun with this equation
23.5 \sin\left(\frac{2\pi(n-81)}{365}\right)
- n is the day of the year
Declination plot
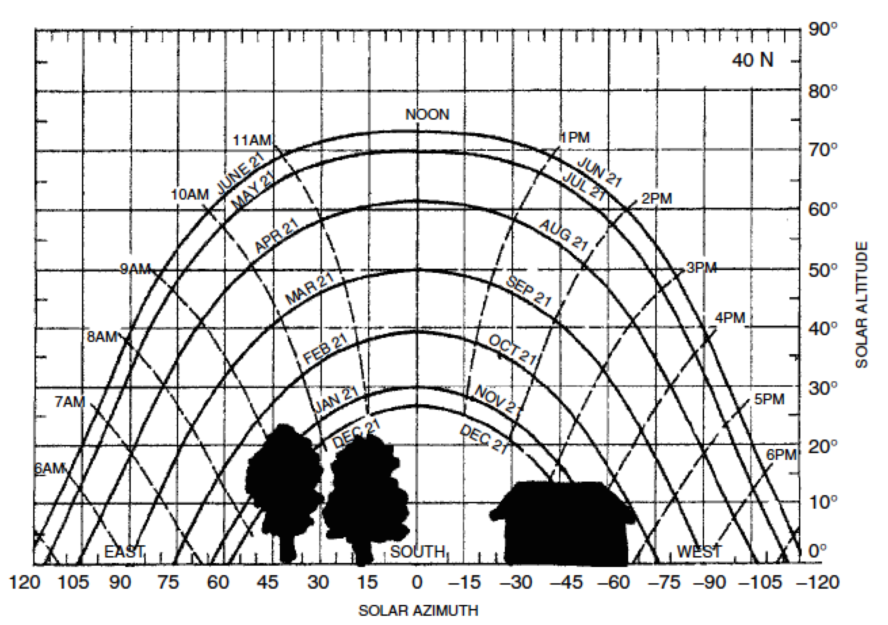
Sun path diagrams
- Do we have to calculate these cumbersome formulas anytime we want to find the sun?
- Oregon Sun Path
- http://solardat.uoregon.edu/SunChartProgram.html
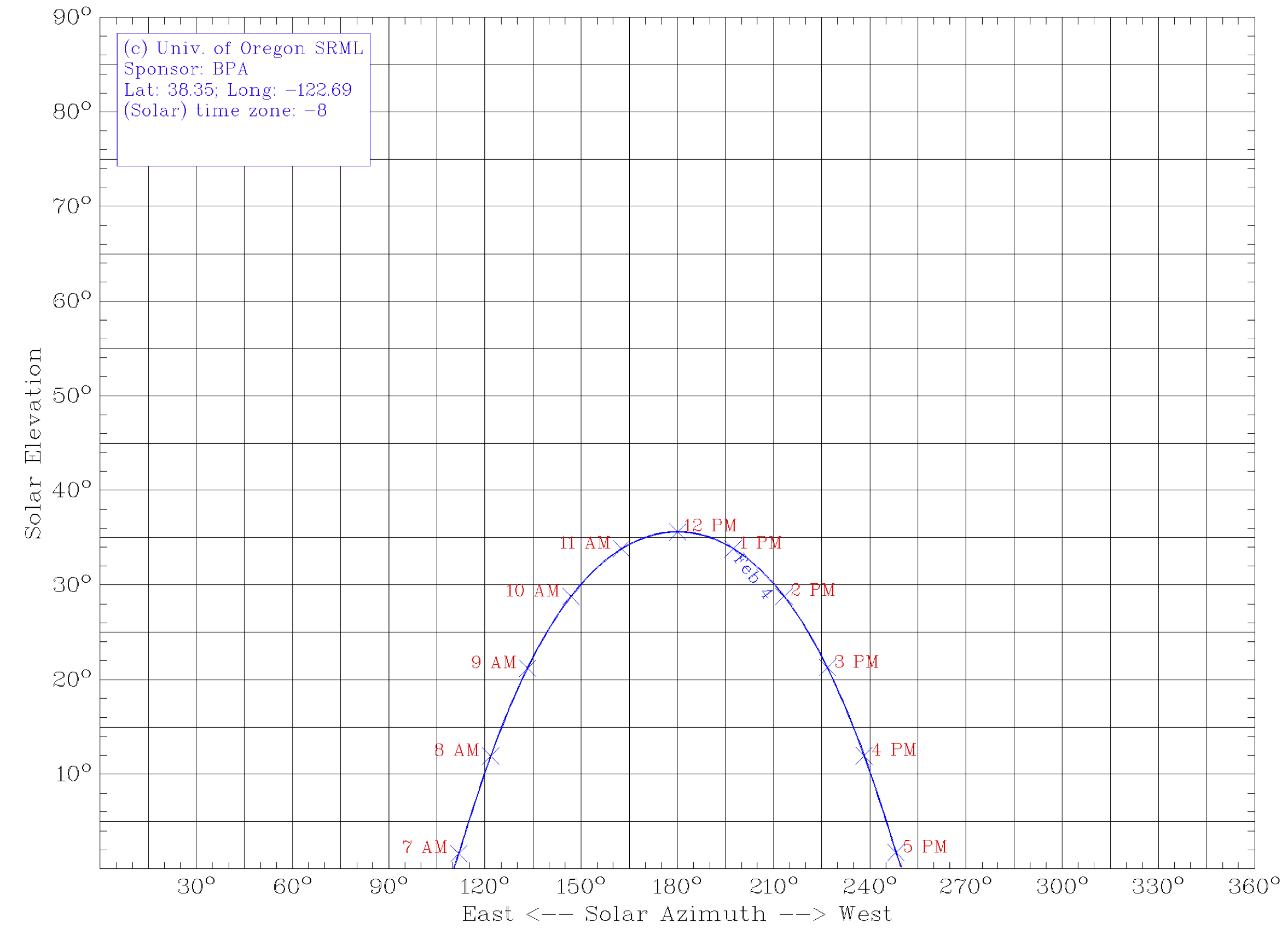
Sun path for February 4
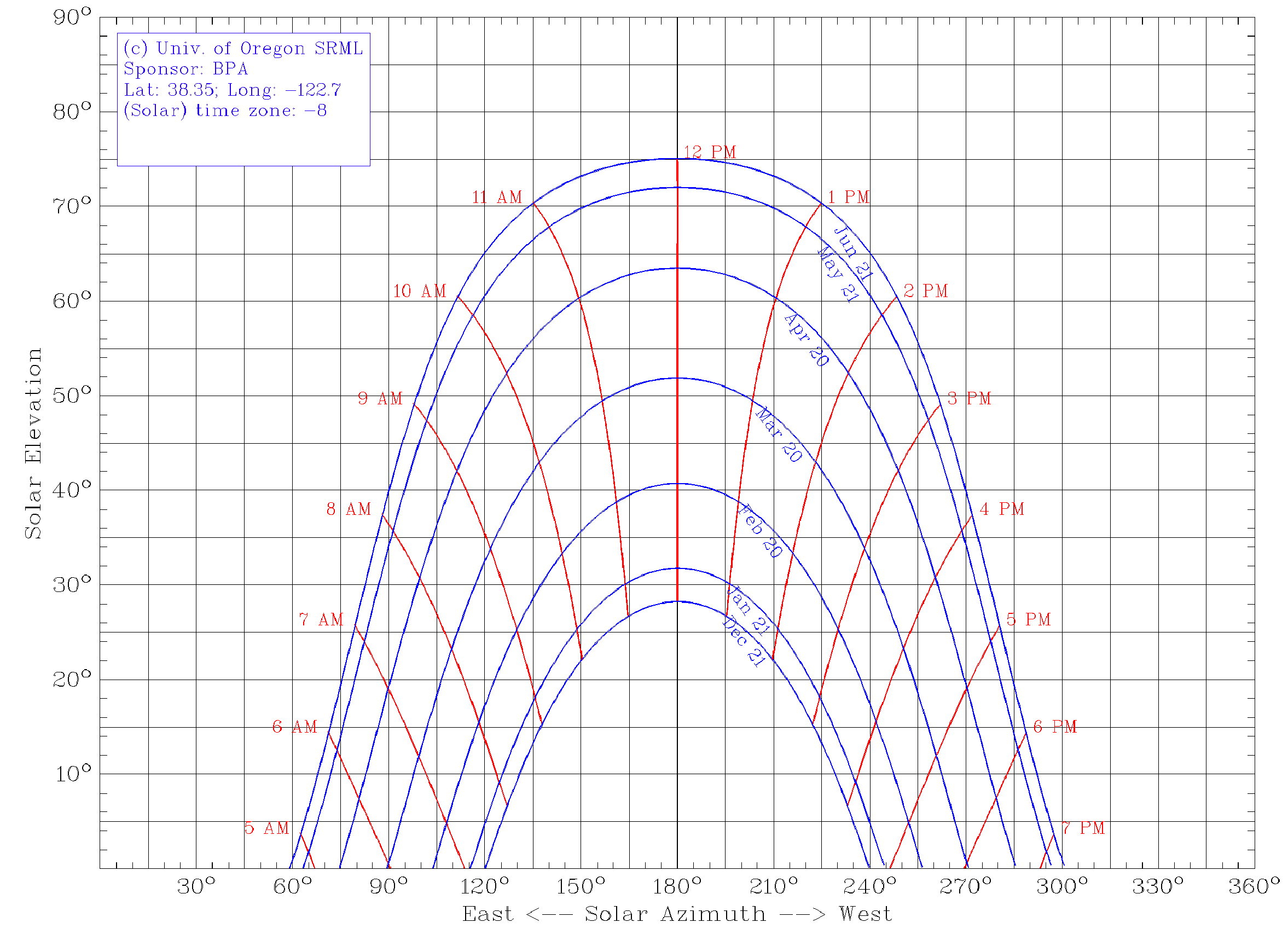
Sun path for SSU
Python Sun Path
Hour angle
H = \frac{15 degrees}{hour} \cdot \textrm{hours before solar noon}
Common panel tilt
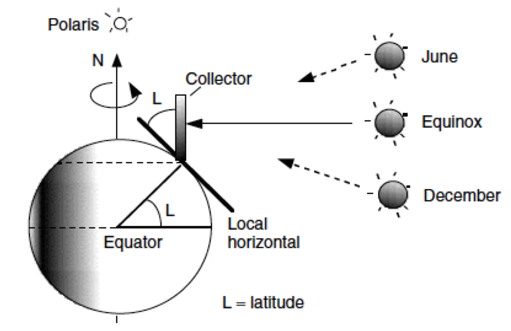
Panels tilted at the latitude so equinox sun strikes directly.
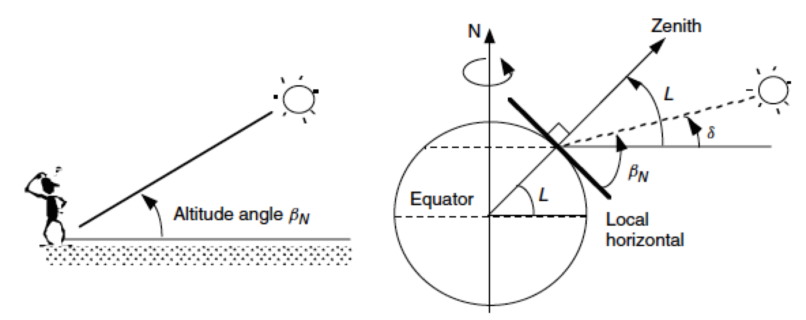
Solar angle calculation
Starting with the day, location, and time, calculate the sun position
(See written notes)
Solar angle measurement
If weather permits, we’ll verify this calculation with a direct measurement.
Solar Angles
- Elevation
- Azimuth
- Relation to architectural features
Solar Elevation
The vertical angle of the sun. Zero degrees at sunset or sunrise. 90 degrees if directly overhead.
Solar Azimuth
The “compass angle” of the sun. Due south at noon (in the northern hemisphere). To the west at sunset. To the east at sunrise.
Solar Declination
The angle of the earths equatorial plane and the plane of the earths orbit. Varies between -23.5 and 23.5 degrees and causes the seasons.
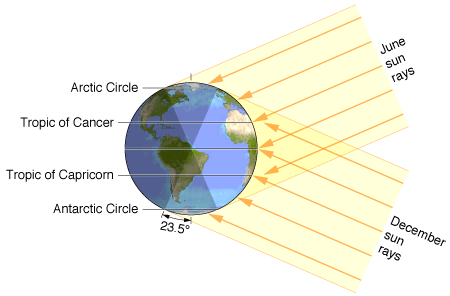
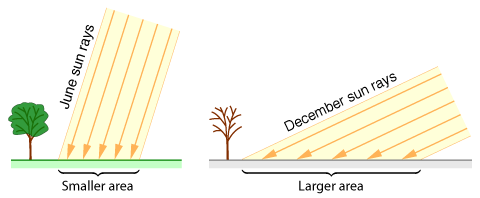
Seasons
- What causes the seasons?
- The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the orbital or ecliptic plane
- This changes the intensity of sunlight in different parts of the globe
- It also changes the distance the rays travel through the atmosphere
Solar position
- How many angles do we need to specify the sun’s position in the sky?
- Elevation
- Azimuth
Hour angle
- Angle of earth rotation with respect to solar noon
Elevation
We measure the vertical angle from the plane of the ground to the sun
\sin\beta = \cos L \cos \delta \cos H + \sin L \sin \delta
- L is the latitude angle
- \delta is the declination angle
- H is the hour angle
Azimuth
We measure the horizontal angle of the sun from north
\sin \phi = \cos \delta \sin H / \cos \beta
- L is the latitude angle
- \delta is the declination angle
- H is the hour angle
Shading Measurements
Path Finder

Software Implementation
You can see an example of these equations implemented in a software library at these locations
- https://github.com/dsoto/PyPVSim
- https://github.com/pvlib/pvlib-python